Page 183 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 183
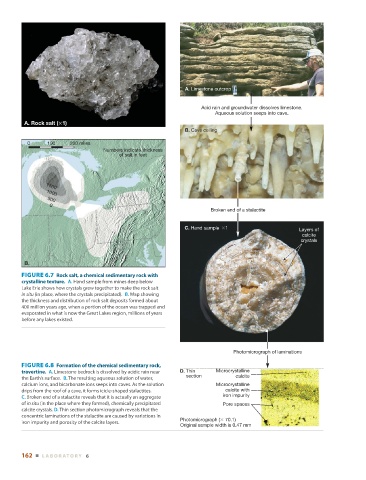
A. Limestone outcrop
Acid rain and groundwater dissolves limestone.
Aqueous solution seeps into cave.
A. Rock salt ( 1)
B. Cave ceiling
0 100 200 miles
Numbers indicate thickness
of salt in feet
1500
1000
500
0
Broken end of a stalactite
C. Hand sample Layers of
calcite
crystals
B.
FIGURE 6.7 Rock salt, a chemical sedimentary rock with
crystalline texture. A. Hand sample from mines deep below
Lake Erie shows how crystals grew together to make the rock salt
in situ (in place, where the crystals precipitated). B. Map showing
the thickness and distribution of rock salt deposits formed about
400 million years ago, when a portion of the ocean was trapped and
evaporated in what is now the Great Lakes region, millions of years
before any lakes existed.
Photomicrograph of laminations
FIGURE 6.8 Formation of the chemical sedimentary rock,
travertine. A. Limestone bedrock is dissolved by acidic rain near D. Thin Microcrystalline
section calcite
the Earth’s surface. B. The resulting aqueous solution of water,
calcium ions, and bicarbonate ions seeps into caves. As the solution Microcrystalline
drips from the roof of a cave, it forms icicle-shaped stalactites. calcite with
C. Broken end of a stalactite reveals that it is actually an aggregate iron impurity
of in situ (in the place where they formed), chemically precipitated Pore spaces
calcite crystals. D. Thin section photomicrograph reveals that the
concentric laminations of the stalactite are caused by variations in
iron impurity and porosity of the calcite layers. Photomicrograph ( 70.1)
Original sample width is 0.47 mm
162 ■ L ABOR ATORY 6