Page 186 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 186
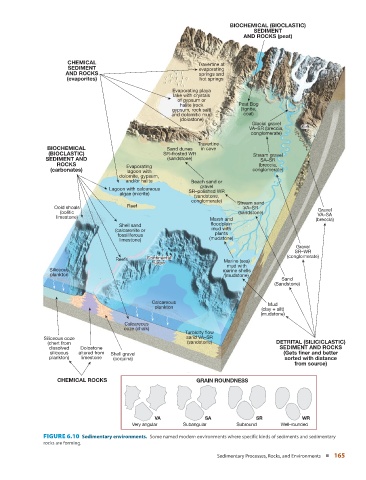
BIOCHEMICAL (BIOCLASTIC)
SEDIMENT
AND ROCKS (peat)
CHEMICAL Travertine at
SEDIMENT evaporating
AND ROCKS springs and
(evaporites) hot springs
Evaporating playa
lake with crystals
of gypsum or
halite (rock Peat Bog
gypsum, rock salt) (lignite,
and dolomitic mud coal)
(dolostone)
Glacial gravel
Cliff
Cli
VA–SR (breccia, Cliff
conglomerate)
Travertine
BIOCHEMICAL Sand dunes in cave
(BIOCLASTIC) SR–frosted WR Stream gravel
SEDIMENT AND (sandstone) SA–SR
ROCKS Evaporating (breccia,
(carbonates) lagoon with conglomerate)
dolomite, gypsum,
and/or halite Beach sand or
gravel
Lagoon with calcareous SR–polished WR
algae (micrite)
(sandstone,
conglomerate) Stream sand
Ooid shoals Reef VA–SR Gravel
(oolitic (sandstone)
limestone) VA–SA
Marsh and (breccia)
Shell sand floodplain
(calcarenite or mud with
fossiliferous plants
limestone) (mudstone)
Gravel
SR–WR
Continental
Continental
Reefs Continental Marine (sea) (conglomerate)
slope
slope
slope
mud with
Siliceous marine shells
plankton (mudstone)
Sand
(Sandstone)
Calcareous Mud
plankton
(clay + silt)
(mudstone)
Calcareous
ooze (chalk)
Turbidity flow
Siliceous ooze sand VA–SR
(chert from (sandstone) DETRITAL (SILICICLASTIC)
dissolved Dolostone SEDIMENT AND ROCKS
siliceous altered from Shell gravel (Gets finer and better
plankton) limestone (coquina) sorted with distance
from source)
CHEMICAL ROCKS GRAIN ROUNDNESS
VA SA SR WR
Very angular Subangular Subround Well-rounded
FIGURE 6.10 Sedimentary environments. Some named modern environments where specific kinds of sediments and sedimentary
rocks are forming.
Sedimentary Processes, Rocks, and Environments ■ 165