Page 191 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 191
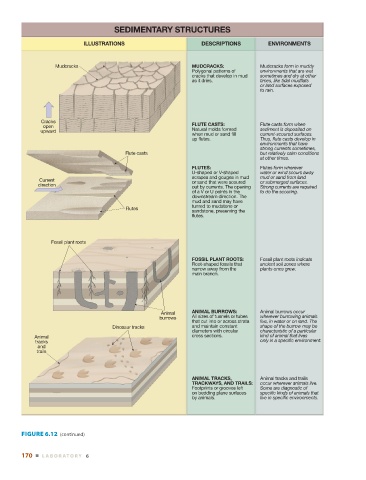
SEDIMENTARY STRUCTURES
ILLUSTRATIONS DESCRIPTIONS ENVIRONMENTS
Mudcracks MUDCRACKS: Mudcracks form in muddy
Polygonal patterns of environments that are wet
cracks that develop in mud sometimes and dry at other
as it dries. times, like tidal mudflats
or land surfaces exposed
to rain.
Cracks
open FLUTE CASTS: Flute casts form when
upward Natural molds formed sediment is deposited on
when mud or sand fill current-scoured surfaces.
up flutes. Thus, flute casts develop in
environments that have
strong currents sometimes,
Flute casts but relatively calm conditions
at other times.
FLUTES: Flutes form wherever
U-shaped or V-shaped water or wind scours away
scrapes and gouges in mud mud or sand from land
Current or sand that were scoured or submerged surfaces.
direction out by currents. The opening Strong currents are required
of a V or U points in the to do the scouring.
downstream direction. The
mud and sand may have
turned to mudstone or
Flutes
sandstone, preserving the
flutes.
Fossil plant roots
FOSSIL PLANT ROOTS: Fossil plant roots indicate
Root-shaped fossils that ancient soil zones where
narrow away from the plants once grew.
main branch.
Animal ANIMAL BURROWS: Animal burrows occur
burrows All sizes of tunnels or tubes wherever burrowing animals
that cut into or across strata live, in water or on land. The
Dinosaur tracks and maintain constant shape of the burrow may be
diameters with circular characteristic of a particular
Animal cross sections. kind of animal that lives
tracks only in a specific environment.
and
trails
ANIMAL TRACKS, Animal tracks and trails
TRACKWAYS, AND TRAILS: occur wherever animals live.
Footprints or grooves left Some are diagnostic of
on bedding plane surfaces specific kinds of animals that
by animals. live in specific environments.
FIGURE 6.12 (continued)
170 ■ L ABOR ATORY 6