Page 94 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 94
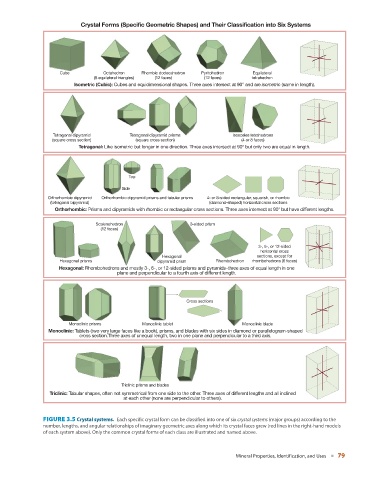
Crystal Forms (Specific Geometric Shapes) and Their Classification into Six Systems
Cube Octahedron Rhombic dodecahedron Pyritohedron Equilateral
(8 equilateral triangles) (12 faces) (12 faces) tetrahedron
Isometric (Cubic): Cubes and equidimensional shapes. Three axes intersect at 90° and are isometric (same in length).
Tetragonal dipyramid Tetragonal dipyramid prisms Isosceles tetrahedrons
(square cross section) (square cross section) (4 or 8 faces)
Tetragonal: Like isometric but longer in one direction. Three axes intersect at 90° but only two are equal in length.
Top
Side
Orthorhombic dipyramid Orthorhombic dipyramid prisms and tabular prisms 4- or 8-sided rectangular, squarish, or rhombic
(tetragonal bipyramid) (diamond-shaped) horizontal cross sections
Orthorhombic: Prisms and dipyramids with rhombic or rectangular cross sections. Three axes intersect at 90° but have different lengths.
Scalenohedron 3-sided prism
(12 faces)
3-, 6-, or 12-sided
horizontal cross
Hexagonal sections, except for
Hexagonal prisms dipyramid prism Rhombohedron rhombohedrons (6 faces)
Hexagonal: Rhombohedrons and mostly 3-, 6-, or 12-sided prisms and pyramids–three axes of equal length in one
plane and perpendicular to a fourth axis of different length.
Cross sections
Monoclinic prisms Monoclinic tablet Monoclinic blade
Monoclinic: Tablets (two very large faces like a book), prisms, and blades with six sides in diamond or parallelogram-shaped
cross section.Three axes of unequal length, two in one plane and perpendicular to a third axis.
Triclinic prisms and blades
Triclinic: Tabular shapes, often not symmetrical from one side to the other. Three axes of different lengths and all inclined
at each other (none are perpendicular to others).
FIGURE 3.5 Crystal systems. Each specific crystal form can be classified into one of six crystal systems (major groups) according to the
number, lengths, and angular relationships of imaginary geometric axes along which its crystal faces grew (red lines in the right-hand models
of each system above). Only the common crystal forms of each class are illustrated and named above.
Mineral Properties, Identification, and Uses ■ 79