Page 44 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 44
A N OVERVIEW OF THE LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT METHOD 25
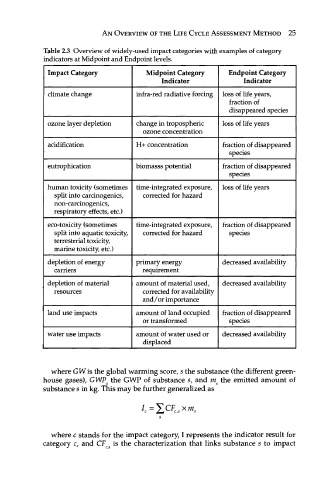
Table 2.3 Overview of widely-used impact categories with examples of category
indicators at Midpoint and Endpoint levels.
Impact Category Midpoint Category Endpoint Category
Indicator Indicator
climate change infra-red radiative forcing loss of life years,
fraction of
disappeared species
ozone layer depletion change in tropospheric loss of life years
ozone concentration
acidification H+ concentration fraction of disappeared
species
eutrophication biomasss potential fraction of disappeared
species
human toxicity (sometimes time-integrated exposure, loss of life years
split into carcinogenics, corrected for hazard
non-carcinogenics,
respiratory effects, etc.)
eco-toxicity (sometimes time-integrated exposure, fraction of disappeared
split into aquatic toxicity, corrected for hazard species
terrestrrial toxicity,
marine toxicity, etc.)
depletion of energy primary energy decreased availability
carriers requirement
depletion of material amount of material used, decreased availability
resources corrected for availability
and/or importance
land use impacts amount of land occupied fraction of disappeared
or transformed species
water use impacts amount of water used or decreased availability
displaced
where GW is the global warming score, s the substance (the different green-
house gases), GWP s the GWP of substance s, and m s the emitted amount of
substance s in kg. This may be further generalized as
s
where c stands for the impact category, I represents the indicator result for
category c, and CF cs is the characterization that links substance s to impact