Page 51 - Lignocellulosic Biomass to Liquid Biofuels
P. 51
30 Lignocellulosic Biomass to Liquid Biofuels
solubilization degree of lignin and hemicelluloses under less severe condi-
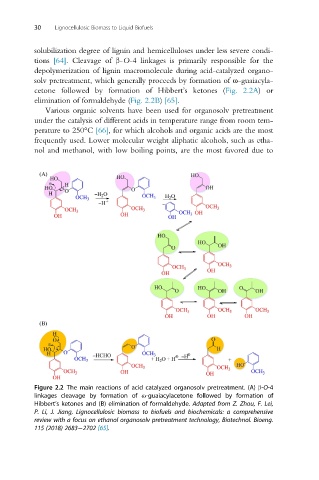
tions [64]. Cleavage of β-O-4 linkages is primarily responsible for the
depolymerization of lignin macromolecule during acid-catalyzed organo-
solv pretreatment, which generally proceeds by formation of ɷ-guaiacyla-
cetone followed by formation of Hibbert’s ketones (Fig. 2.2A)or
elimination of formaldehyde (Fig. 2.2B) [65].
Various organic solvents have been used for organosolv pretreatment
under the catalysis of different acids in temperature range from room tem-
perature to 250°C [66], for which alcohols and organic acids are the most
frequently used. Lower molecular weight aliphatic alcohols, such as etha-
nol and methanol, with low boiling points, are the most favored due to
Figure 2.2 The main reactions of acid catalyzed organosolv pretreatment. (A) β-O-4
linkages cleavage by formation of ɷ-guaiacylacetone followed by formation of
Hibbert’s ketones and (B) elimination of formaldehyde. Adapted from Z. Zhou, F. Lei,
P. Li, J. Jiang, Lignocellulosic biomass to biofuels and biochemicals: a comprehensive
review with a focus on ethanol organosolv pretreatment technology, Biotechnol. Bioeng.
115 (2018) 2683 2702 [65].