Page 54 - Lignocellulosic Biomass to Liquid Biofuels
P. 54
Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for efficient enzymatic saccharification of cellulose 33
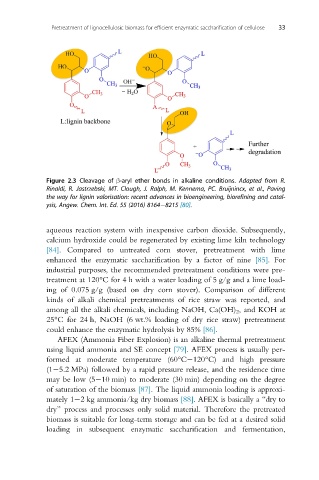
Figure 2.3 Cleavage of β-aryl ether bonds in alkaline conditions. Adapted from R.
Rinaldi, R. Jastrzebski, MT. Clough, J. Ralph, M. Kennema, PC. Bruijnincx, et al., Paving
the way for lignin valorisation: recent advances in bioengineering, biorefining and catal-
ysis, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55 (2016) 8164 8215 [80].
aqueous reaction system with inexpensive carbon dioxide. Subsequently,
calcium hydroxide could be regenerated by existing lime kiln technology
[84]. Compared to untreated corn stover, pretreatment with lime
enhanced the enzymatic saccharification by a factor of nine [85]. For
industrial purposes, the recommended pretreatment conditions were pre-
treatment at 120°C for 4 h with a water loading of 5 g/g and a lime load-
ing of 0.075 g/g (based on dry corn stover). Comparison of different
kinds of alkali chemical pretreatments of rice straw was reported, and
among all the alkali chemicals, including NaOH, Ca(OH) 2 , and KOH at
25°C for 24 h, NaOH (6 wt.% loading of dry rice straw) pretreatment
could enhance the enzymatic hydrolysis by 85% [86].
AFEX (Ammonia Fiber Explosion) is an alkaline thermal pretreatment
using liquid ammonia and SE concept [79]. AFEX process is usually per-
formed at moderate temperature (60°C 120°C) and high pressure
(1 5.2 MPa) followed by a rapid pressure release, and the residence time
may be low (5 10 min) to moderate (30 min) depending on the degree
of saturation of the biomass [87]. The liquid ammonia loading is approxi-
mately 1 2 kg ammonia/kg dry biomass [88]. AFEX is basically a “dry to
dry” process and processes only solid material. Therefore the pretreated
biomass is suitable for long-term storage and can be fed at a desired solid
loading in subsequent enzymatic saccharification and fermentation,