Page 197 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 197
8.10 PRIMARY BATTERIES
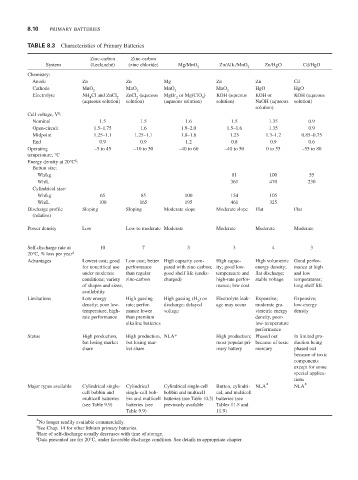
TABLE 8.3 Characteristics of Primary Batteries
Zinc-carbon Zinc-carbon
System (Leclanché) (zinc chloride) Mg/MnO 2 Zn/Alk./MnO 2 Zn/HgO Cd/HgO Zn/Ag O Zinc/air Li/SO 2 † Li/SOCl 2 † Li/MnO 2 † Li/FeS 2 † Solid state
2
Chemistry:
Anode Zn Zn Mg Zn Zn Cd Zn Li Li Li Li Li
Cathode MnO 2 MnO 2 MnO 2 MnO 2 HgO HgO Ag O or AgO O (air) SO 2 SOCl 2 MnO 2 FeS 2 I (P2VP)
2
2
2
Electrolyte NH Cl and ZnCl 2 ZnCl (aqueous MgBr or Mg(ClO ) KOH (aqueous KOH or KOH (aqueous KOH or NaOH KOH (aqueous Organic solvent, SOCl w/AlCl 4 Organic solvent, salt Organic solvent, Solid
4
2
2
4
2
(aqueous solution) solution) (aqueous solution) solution) NaOH (aqueous solution) (aqueous solution) salt solution solution salt solution
solution) solution)
§
Cell voltage, V :
Nominal 1.5 1.5 1.6 1.5 1.35 0.9 1.5 1.5 3.0 3.6 3.0 1.5 2.8
Open-circuit 1.5–1.75 1.6 1.9–2.0 1.5–1.6 1.35 0.9 1.6 1.45 3.1 3.65 3.3 1.8 2.8
Midpoint 1.25–1.1 1.25–1.1 1.8–1.6 1.23 1.3–1.2 0.85–0.75 1.6–1.5 1.3–1.1 2.9–2.75 3.6–3.3 3.0–2.7 1.6–1.4 2.8–2.6
End 0.9 0.9 1.2 0.8 0.9 0.6 1.0 0.9 2.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 2.0
Operating –5 to 45 –10 to 50 –40 to 60 –40 to 50 0 to 55 –55 to 80 0 to 55 0 to 50 –55 to 70 –60 to 85 –20 to 55 –20 to 60 0 to 200
temperature, °C
§
Energy density at 20°C :
Button size:
Wh/kg 81 100 55 135 415 230
Wh/L 361 470 230 530 1350 545
Cylindrical size: Bobbin Spiral-wound Bobbin Spiral-wound
Wh/kg 65 85 100 154 105 Prismatic 500 260 590 495 270 261 310 220–280
Wh/L 100 165 195 461 325 Prismatic 1250 415 1100 970 620 546 560 820–1030
Discharge profile Sloping Sloping Moderate slope Moderate slope Flat Flat Flat Flat Very flat Flat Flat Medium to high Moderately flat
(relative) (at low discharge
rates)
Power density Low Low to moderate Moderate Moderate Moderate Moderate Moderate Low High Medium (but depen- Moderate Medium to high Very low
dent on specific
design)
Self-discharge rate at 10 7 3 3 4 3 6 3 (if sealed) 2 1–2 1–2 1–2 <1
20°C, % loss per year ‡
Advantages Lowest cost; good Low cost; better High capacity com- High capac- High volumetric Good perfor- High energy High volumetric High energy High energy density; High energy density; Replacement for Excellent shelf
for noncritical use performance pared with zinc-carbon; ity; good low- energy density; mance at high density; good energy density; density; best low- long shelf life because good low-temperature, Zu/alkaline/MnO life (10–20 y);
2
under moderate than regular good shelf life (undis- temperature and flat discharge; and low high-rate long shelf life temperature, high- of protective film high-rate performance; batteries for high- wide operating
conditions; variety zinc-carbon charged) high-rate perfor- stable voltage temperatures; performance (sealed) rate performance; cost-effective replace- rate performance temperature range
of shapes and sizes; mance; low cost long shelf life long shelf life ment for small conven- (to 200°C)
availability tional type cells
Limitations Low energy High gassing High gassing (H ) on Electrolyte leak- Expensive; Expensive; Expensive, but Not independent Pressurized system; Voltage delay after Available in small Higher cost than For very low dis-
2
density; poor low- rate; perfor- discharge; delayed age may occur moderate gra- low-energy cost-effective on of environment— potential safety storage sizes; larger sizes being alkaline batteries charge rates; poor
temperature, high- mance lower voltage vimetric energy density button battery flooding, drying problems; toxic considered; shipment low temperature
rate performance than premium density, poor- applications out; limited components; regulated performance
alkaline batteries low-temperature power output shipment regulated
performance
Status High production, High production, NLA* High production; Phased out In limited pro- In production Moderate pro- Moderate pro- Produced in wide Increasing consumer Produced in AAA In production
but losing market but losing mar- most popular pri- because of toxic duction being duction; key use duction, mainly range of sizes and production and AA sizes; 9 V for special
share ket share mary battery mercury phased out in hearing aids military designs; mainly for batteries also applications
because of toxic special available
components applications
except for some
special applica-
tions
Major types available Cylindrical single- Cylindrical Cylindrical single-cell Button, cylindri- NLA * NLA * Button batteries (See Tables 13.5 Cylindrical batter- (See Sec. 14.6 and Button and small Cylindrical cells (See Sec 31.5.)
cell bobbin and single-cell bob- bobbin and multicell cal, and multicell (see Table 13.3) and 13.6, also ies (see Tables 14.9 Tables 14.11 to 14.13) cylindrical batteries and 9 V (see
multicell batteries bin and multicell batteries (see Table 10.3) batteries (see Chap. 33) and 14.10) (see Tables 14.10 and Table 14.23)
(see Table 9.9) batteries (see previously available Tables 11.8 and 14.18–14.20)
Table 9.9) 11.9)
* No longer readily available commercially.
† See Chap. 14 for other lithium primary batteries.
‡ Rate of self-discharge usually decreases with time of storage.
§ Data presented are for 20°C, under favorable discharge condition. See details in appropriate chapter.