Page 242 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 242
9.36 PRIMARY BATTERIES
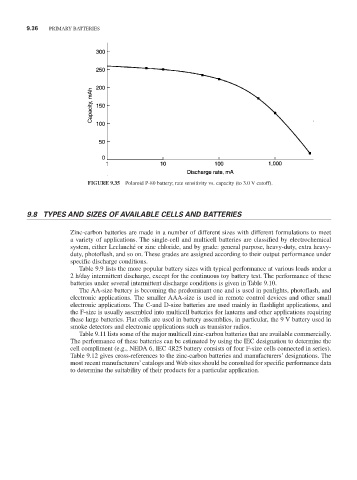
FIGURE 9.35 Polaroid P-80 battery; rate sensitivity vs. capacity (to 3.0 V cutoff).
9.8 TYPES AND SIZES OF AVAILABLE CELLS AND BATTERIES
Zinc-carbon batteries are made in a number of different sizes with different formulations to meet
a variety of applications. The single-cell and multicell batteries are classified by electrochemical
system, either Leclanché or zinc chloride, and by grade: general purpose, heavy-duty, extra heavy-
duty, photoflash, and so on. These grades are assigned according to their output performance under
specific discharge conditions.
Table 9.9 lists the more popular battery sizes with typical performance at various loads under a
2 h/day intermittent discharge, except for the continuous toy battery test. The performance of these
batteries under several intermittent discharge conditions is given in Table 9.10.
The AA-size battery is becoming the predominant one and is used in penlights, photoflash, and
electronic applications. The smaller AAA-size is used in remote control devices and other small
electronic applications. The C-and D-size batteries are used mainly in flashlight applications, and
the F-size is usually assembled into multicell batteries for lanterns and other applications requiring
these large batteries. Flat cells are used in battery assemblies, in particular, the 9 V battery used in
smoke detectors and electronic applications such as transistor radios.
Table 9.11 lists some of the major multicell zinc-carbon batteries that are available commercially.
The performance of these batteries can be estimated by using the IEC designation to determine the
cell compliment (e.g., NEDA 6, IEC 4R25 battery consists of four F-size cells connected in series).
Table 9.12 gives cross-references to the zinc-carbon batteries and manufacturers’ designations. The
most recent manufacturers’ catalogs and Web sites should be consulted for specific performance data
to determine the suitability of their products for a particular application.