Page 26 - MATLAB an introduction with applications
P. 26
MATLAB Basics ——— 11
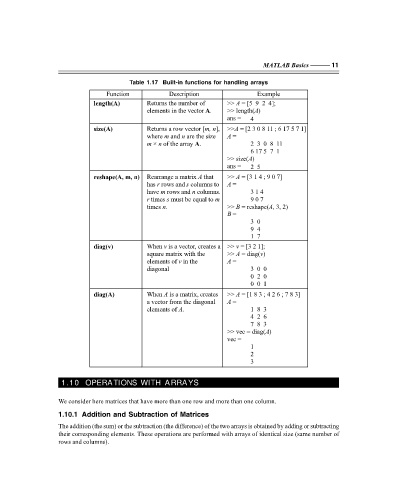
Table 1.17 Built-in functions for handling arrays
Function Description Example
length(A) Returns the number of >> = [5 9 2 4];
A
elements in the vector A. >> length( )
A
ans = 4
size( )A Returns a row vector [m, n ], >> = [2 3 0 8 11 ; 6 17 5 7 1]A
m
where and are the size A =
n
m × n of the array A. 2 3 0 8 11
6 17 5 7 1
>> size( )
A
ans = 2 5
A
reshape(A, m, n) Rearrange a matrix that >> = [3 1 4 ; 9 0 7]
A
s
has rows and columns to A =
r
m
have rows and columns. 3 1 4
n
r times s must be equal to m 9 0 7
times . >> = reshape( , 3, 2)
n
B
A
B =
3 0
9 4
1 7
v
diag(v) When is a vector, creates a >> = [3 2 1];v
A
v
square matrix with the >> = diag( )
elements of in the A =
v
diagonal 3 0 0
0 2 0
0 0 1
A
diag(A) When is a matrix, creates >> = [1 8 3 ; 4 2 6 ; 7 8 3]
A
a vector from the diagonal A =
elements of . 1 8 3
A
4 2 6
7 8 3
>> vec = diag( )
A
vec =
1
2
3
1.10 OPERATIONS WITH ARRAYS
We consider here matrices that have more than one row and more than one column.
1.10.1 Addition and Subtraction of Matrices
The addition (the sum) or the subtraction (the difference) of the two arrays is obtained by adding or subtracting
their corresponding elements. These operations are performed with arrays of identical size (same number of
rows and columns).
F:\Final Book\Sanjay\IIIrd Printout\Dt. 10-03-09