Page 30 - MATLAB an introduction with applications
P. 30
MATLAB Basics ——— 15
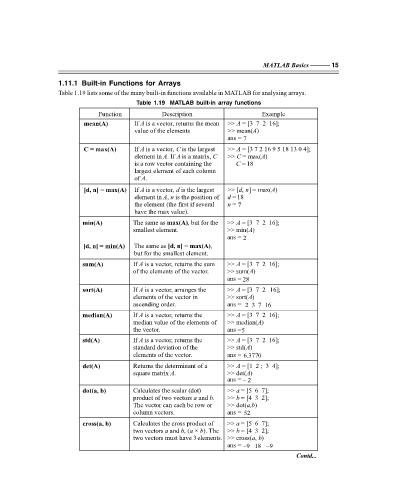
1.11.1 Built-in Functions for Arrays
Table 1.19 lists some of the many built-in functions available in MATLAB for analysing arrays.
Table 1.19 MATLAB built-in array functions
Function Description Example
A
mean(A) If A is a vector, returns the mean >> = [3 7 2 16];
value of the elements >> mean( )
A
ans = 7
C = max(A) If A is a vector, C is the largest >> = [3 7 2 16 9 5 18 13 0 4];
A
element in A. If A is a matrix, C >> = max( )
C
A
is a row vector containing the C = 18
largest element of each column
of A.
[d, n] = max(A) If A is a vector, d is the largest >> [ , dn] = max( A)
element in A, n is the position of d = 18
the element (the first if several n = 7
have the max value).
min(A) The same as max(A), but for the >> = [3 7 2 16];
A
smallest element. >> min( )
A
ans = 2
[d, n] = min( ) The same as [d, n] = max(A),
A
but for the smallest element.
A
sum( )A If A is a vector, returns the sum >> = [3 7 2 16];
of the elements of the vector. >> sum( )
A
ans = 28
sort( )A If A is a vector, arranges the >> = [3 7 2 16];
A
elements of the vector in >> sort( )
A
ascending order. ans = 2 3 7 16
A
median( )A If A is a vector, returns the >> = [3 7 2 16];
median value of the elements of >> median( )
A
the vector. ans = 5
A
std( )A If A is a vector, returns the >> = [3 7 2 16];
standard deviation of the >> std( )
A
elements of the vector. ans = 6.3770
det( )A Returns the determinant of a >> = [1 2 ; 3 4];
A
A
square matrix A. >> det( )
ans = – 2
a
dot(a, b) Calculates the scalar (dot) >> = [5 6 7];
product of two vectors a and b. >> = [4 3 2];
b
The vector can each be row or >> dot(a,b )
column vectors. ans = 52
a
cross(a, b) Calculates the cross product of >> = [5 6 7];
two vectors a and b, (a × b). The >> = [4 3 2];
b
two vectors must have 3 elements. >> cross( , )
ab
ans = –9 18 –9
Contd...
F:\Final Book\Sanjay\IIIrd Printout\Dt. 10-03-09