Page 65 - Macromolecular Crystallography
P. 65
54 MACROMOLECULAR CRYS TALLOGRAPHY
3.6 Control of the evaporation kinetics
(a) of vapour diffusion trials
Thin layer of
paraffin oil The formation of numerous, small crystals instead
of the desired large single ones can occur due to
the crystallization process taking place too rapidly.
A means to slow down the equilibration rate in
vapour diffusion and thereby approach supersatu-
Crystallization ration more slowly in order to avoid the formation
drop
of ‘showers’, twinned crystals, or precipitate, is
by placing a mixture of paraffin and silicone oils
as a barrier over the reservoirs of hanging or sit-
ting drop trials (Chayen, 1997b). Paraffin oil totally
blocks all vapour diffusion, resulting in drying out
(b) of the drops, while silicon oil allows diffusion to
take place fully. The equilibration rate is therefore
Dispenser
dictated by the ratio of the two oils and by the
thickness of the oil–mixture layer (Protocol 3.8).
Thick layer of
paraffin oil Equal volumes of paraffin and silicon, in a layer
of 250–500 µl, placed over 0.6–1 ml reservoirs in
Linbro type plates were found to be optimal. This
method has been successful in crystallizing prob-
lematic target proteins (e.g. Mandelman et al., 2002;
Isupov et al., 2004). The advantage of this technique
is that no change is required to the crystallization
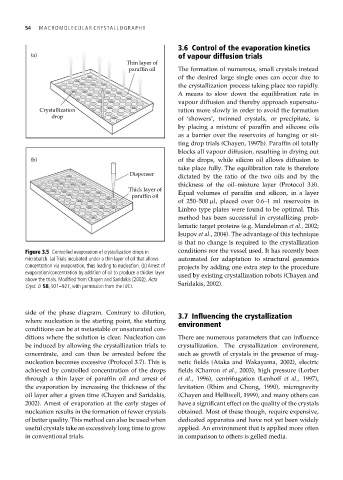
Figure 3.5 Controlled evaporation of crystallization drops in conditions nor the vessel used. It has recently been
microbatch. (a) Trials incubated under a thin layer of oil that allows automated for adaptation to structural genomics
concentration via evaporation, thus leading to nucleation. (b) Arrest of projects by adding one extra step to the procedure
evaporation/concentration by addition of oil to produce a thicker layer used by existing crystallization robots (Chayen and
above the trials. Modified from Chayen and Saridakis (2002), Acta
Cryst. D 58, 921–927, with permission from the IUCr. Saridakis, 2002).
side of the phase diagram. Contrary to dilution, 3.7 Influencing the crystallization
where nucleation is the starting point, the starting environment
conditions can be at metastable or unsaturated con-
ditions where the solution is clear. Nucleation can There are numerous parameters that can influence
be induced by allowing the crystallization trials to crystallization. The crystallization environment,
concentrate, and can then be arrested before the such as growth of crystals in the presence of mag-
nucleation becomes excessive (Protocol 3.7). This is netic fields (Ataka and Wakayama, 2002), electric
achieved by controlled concentration of the drops fields (Charron et al., 2003), high pressure (Lorber
through a thin layer of paraffin oil and arrest of et al., 1996), centrifugation (Lenhoff et al., 1997),
the evaporation by increasing the thickness of the levitation (Rhim and Chung, 1990), microgravity
oil layer after a given time (Chayen and Saridakis, (Chayen and Helliwell, 1999), and many others can
2002). Arrest of evaporation at the early stages of have a significant effect on the quality of the crystals
nucleation results in the formation of fewer crystals obtained. Most of these though, require expensive,
of better quality. This method can also be used when dedicated apparatus and have not yet been widely
useful crystals take an excessively long time to grow applied. An environment that is applied more often
in conventional trials. in comparison to others is gelled media.