Page 202 -
P. 202
Chapter 5 IT Infrastructure and Emerging Technologies 201
remotely. Software firms such as Google, Microsoft, SAP, Oracle, and Salesforce.
com sell software applications as services delivered over the Internet.
We discuss cloud and mobile computing in more detail in Section 5.3. The
Learning Tracks include a table titled Comparing Stages in IT Infrastructure
Evolution, which compares each era on the infrastructure dimensions introduced.
TECHNOLOGY DRIVERS OF INFRASTRUCTURE
EVOLUTION
The changes in IT infrastructure we have just described have resulted from
developments in computer processing, memory chips, storage devices,
telecommunications and networking hardware and software, and software
design that have exponentially increased computing power while exponentially
reducing costs. Let’s look at the most important developments.
Moore’s Law and Microprocessing Power
In 1965, Gordon Moore, the director of Fairchild Semiconductor’s Research and
Development Laboratories, an early manufacturer of integrated circuits, wrote
in Electronics magazine that since the first microprocessor chip was introduced
in 1959, the number of components on a chip with the smallest manufacturing
costs per component (generally transistors) had doubled each year. This asser-
tion became the foundation of Moore’s Law. Moore later reduced the rate of
growth to a doubling every two years.
This law would later be interpreted in multiple ways. There are at least three
variations of Moore’s Law, none of which Moore ever stated: (1) the power of
microprocessors doubles every 18 months; (2) computing power doubles every
18 months; and (3) the price of computing falls by half every 18 months.
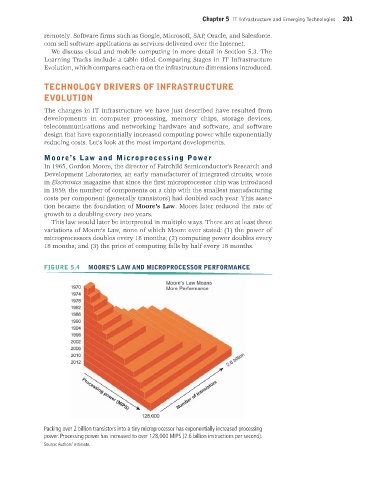
FIGURE 5.4 MOORE’S LAW AND MICROPROCESSOR PERFORMANCE
Packing over 2 billion transistors into a tiny microprocessor has exponentially increased processing
power. Processing power has increased to over 128,000 MIPS (2.6 billion instructions per second).
Source: Authors’ estimate.
MIS_13_Ch_05_Global.indd 201 1/17/2013 3:04:21 PM