Page 205 -
P. 205
204 Part Two Information Technology Infrastructure
Metcalfe’s Law and Network Economics
Moore’s Law and the Law of Mass Storage help us understand why computing
resources are now so readily available. But why do people want more com-
puting and storage power? The economics of networks and the growth of the
Internet provide some answers.
Robert Metcalfe—inventor of Ethernet local area network technology—
claimed in 1970 that the value or power of a network grows exponentially
as a function of the number of network members. Metcalfe and others point
to the increasing returns to scale that network members receive as more and
more people join the network. As the number of members in a network grows
linearly, the value of the entire system grows exponentially and continues to
grow forever as members increase. Demand for information technology has
been driven by the social and business value of digital networks, which rapidly
multiply the number of actual and potential links among network members.
Declining Communications Costs and the Internet
A fourth technology driver transforming IT infrastructure is the rapid decline
in the costs of communication and the exponential growth in the size of the
Internet. An estimated 2.3 billion people worldwide now have Internet access
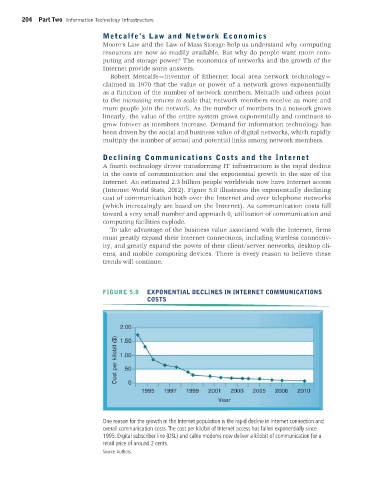
(Internet World Stats, 2012). Figure 5.8 illustrates the exponentially declining
cost of communication both over the Internet and over telephone networks
(which increasingly are based on the Internet). As communication costs fall
toward a very small number and approach 0, utilization of communication and
computing facilities explode.
To take advantage of the business value associated with the Internet, firms
must greatly expand their Internet connections, including wireless connectiv-
ity, and greatly expand the power of their client/server networks, desktop cli-
ents, and mobile computing devices. There is every reason to believe these
trends will continue.
FIGURE 5.8 EXPONENTIAL DECLINES IN INTERNET COMMUNICATIONS
COSTS
One reason for the growth in the Internet population is the rapid decline in Internet connection and
overall communication costs. The cost per kilobit of Internet access has fallen exponentially since
1995. Digital subscriber line (DSL) and cable modems now deliver a kilobit of communication for a
retail price of around 2 cents.
Source: Authors.
MIS_13_Ch_05_Global.indd 204 1/17/2013 3:04:24 PM