Page 288 -
P. 288
Chapter 7 Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology 287
network without a dedicated server. The Windows domain network model, in
contrast, uses a dedicated server to manage the computers in the network.
Larger LANs have many clients and multiple servers, with separate servers
for specific services, such as storing and managing files and databases (file
servers or database servers), managing printers (print servers), storing and
managing e-mail (mail servers), or storing and managing Web pages (Web
servers).
Metropolitan and Wide Area Networks
Wide area networks (WANs) span broad geographical distances—entire
regions, states, continents, or the entire globe. The most universal and powerful
WAN is the Internet. Computers connect to a WAN through public networks,
such as the telephone system or private cable systems, or through leased lines
or satellites. A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a network that spans a
metropolitan area, usually a city and its major suburbs. Its geographic scope
falls between a WAN and a LAN.
TRANSMISSION MEDIA AND TRANSMISSION SPEED
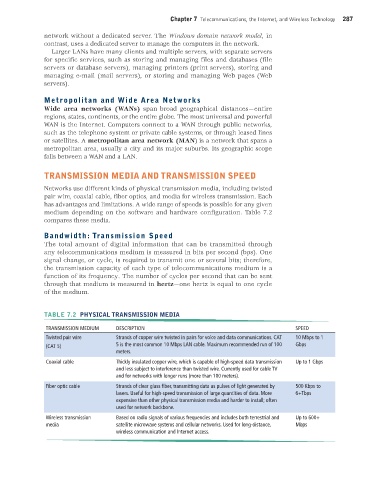
Networks use different kinds of physical transmission media, including twisted
pair wire, coaxial cable, fiber optics, and media for wireless transmission. Each
has advantages and limitations. A wide range of speeds is possible for any given
medium depending on the software and hardware configuration. Table 7.2
compares these media.
Bandwidth: Transmission Speed
The total amount of digital information that can be transmitted through
any telecommunications medium is measured in bits per second (bps). One
signal change, or cycle, is required to transmit one or several bits; therefore,
the transmission capacity of each type of telecommunications medium is a
function of its frequency. The number of cycles per second that can be sent
through that medium is measured in hertz—one hertz is equal to one cycle
of the medium.
TABLE 7.2 PHYSICAL TRANSMISSION MEDIA
TRANSMISSION MEDIUM DESCRIPTION SPEED
Twisted pair wire Strands of copper wire twisted in pairs for voice and data communications. CAT 10 Mbps to 1
(CAT 5) 5 is the most common 10 Mbps LAN cable. Maximum recommended run of 100 Gbps
meters.
Coaxial cable Thickly insulated copper wire, which is capable of high-speed data transmission Up to 1 Gbps
and less subject to interference than twisted wire. Currently used for cable TV
and for networks with longer runs (more than 100 meters).
Fiber optic cable Strands of clear glass fiber, transmitting data as pulses of light generated by 500 Kbps to
lasers. Useful for high-speed transmission of large quantities of data. More 6+Tbps
expensive than other physical transmission media and harder to install; often
used for network backbone.
Wireless transmission Based on radio signals of various frequencies and includes both terrestrial and Up to 600+
media satellite microwave systems and cellular networks. Used for long-distance, Mbps
wireless communication and Internet access.
MIS_13_Ch_07_Global.indd 287 1/17/2013 2:28:30 PM