Page 486 -
P. 486
Chapter 12 Enhancing Decision Making 485
12.1 DECISION MAKING AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Decision making in businesses used to be limited to management. Today,
lower-level employees are responsible for some of these decisions, as informa-
tion systems make information available to lower levels of the business. But
what do we mean by better decision making? How does decision making take
place in businesses and other organizations? Let’s take a closer look.
BUSINESS VALUE OF IMPROVED DECISION MAKING
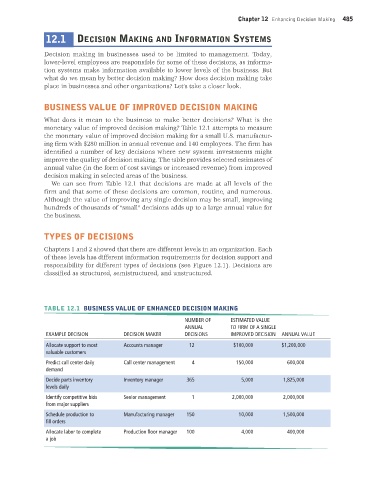
What does it mean to the business to make better decisions? What is the
monetary value of improved decision making? Table 12.1 attempts to measure
the monetary value of improved decision making for a small U.S. manufactur-
ing firm with $280 million in annual revenue and 140 employees. The firm has
identified a number of key decisions where new system investments might
improve the quality of decision making. The table provides selected estimates of
annual value (in the form of cost savings or increased revenue) from improved
decision making in selected areas of the business.
We can see from Table 12.1 that decisions are made at all levels of the
firm and that some of these decisions are common, routine, and numerous.
Although the value of improving any single decision may be small, improving
hundreds of thousands of “small” decisions adds up to a large annual value for
the business.
TYPES OF DECISIONS
Chapters 1 and 2 showed that there are different levels in an organization. Each
of these levels has different information requirements for decision support and
responsibility for different types of decisions (see Figure 12.1). Decisions are
classified as structured, semistructured, and unstructured.
TABLE 12.1 BUSINESS VALUE OF ENHANCED DECISION MAKING
NUMBER OF ESTIMATED VALUE
ANNUAL TO FIRM OF A SINGLE
EXAMPLE DECISION DECISION MAKER DECISIONS IMPROVED DECISION ANNUAL VALUE
Allocate support to most Accounts manager 12 $100,000 $1,200,000
valuable customers
Predict call center daily Call center management 4 150,000 600,000
demand
Decide parts inventory Inventory manager 365 5,000 1,825,000
levels daily
Identify competitive bids Senior management 1 2,000,000 2,000,000
from major suppliers
Schedule production to Manufacturing manager 150 10,000 1,500,000
fill orders
Allocate labor to complete Production floor manager 100 4,000 400,000
a job
MIS_13_Ch_12 global.indd 485 1/17/2013 2:30:29 PM