Page 221 - Managing Global Warming
P. 221
Current and future nuclear power reactors and plants 181
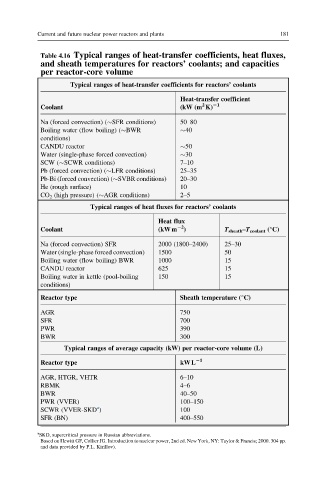
Table 4.16 Typical ranges of heat-transfer coefficients, heat fluxes,
and sheath temperatures for reactors’ coolants; and capacities
per reactor-core volume
Typical ranges of heat-transfer coefficients for reactors’ coolants
Heat-transfer coefficient
2 21
Coolant (kW (m K)
Na (forced convection) ( SFR conditions) 50–80
Boiling water (flow boiling) ( BWR 40
conditions)
CANDU reactor 50
Water (single-phase forced convection) 30
SCW ( SCWR conditions) 7–10
Pb (forced convection) ( LFR conditions) 25–35
Pb-Bi (forced convection) ( SVBR conditions) 20–30
He (rough surface) 10
CO 2 (high pressure) ( AGR conditions) 2–5
Typical ranges of heat fluxes for reactors’ coolants
Heat flux
22
Coolant (kWm ) T sheath –T coolant (°C)
Na (forced convection) SFR 2000 (1800–2400) 25–30
Water (single-phase forced convection) 1500 50
Boiling water (flow boiling) BWR 1000 15
CANDU reactor 625 15
Boiling water in kettle (pool-boiling 150 15
conditions)
Reactor type Sheath temperature (°C)
AGR 750
SFR 700
PWR 390
BWR 300
Typical ranges of average capacity (kW) per reactor-core volume (L)
21
Reactor type kWL
AGR, HTGR, VHTR 6–10
RBMK 4–6
BWR 40–50
PWR (VVER) 100–150
a
SCWR (VVER-SKD ) 100
SFR (BN) 400–550
a
SKD, supercritical pressure in Russian abbreviations.
Based on Hewitt GF, Collier JG. Introduction to nuclear power, 2nd ed. New York, NY: Taylor & Francis; 2000. 304 pp.
and data provided by P.L. Kirillov).