Page 325 - Manufacturing Engineering and Technology - Kalpakjian, Serope : Schmid, Steven R.
P. 325
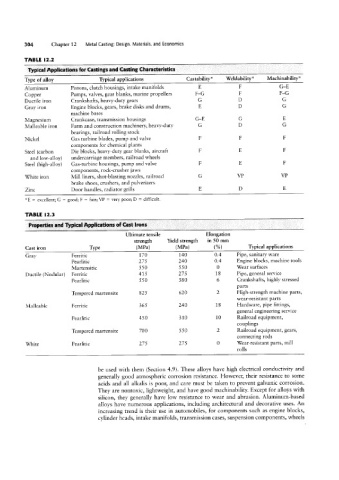
304 Chapter 12 Metal Casting: Design, Materials, and Economics
TABLE l2.2
Typical Applications for Castings and Casting Characteristics
Type of alloy Typical applications Castability* Weldability* Machinability*
Aluminum Pistons, clutch housings, intake manifolds E F G-E
Copper Pumps, valves, gear blanks, marine propellers F-G F F-G
Ductile iron Crankshafts, heavy-duty gears G D G
Gray iron Engine blocks, gears, brake disks and drums, E D G
machine bases
Magnesium Crankcase, transmission housings G-E G E
Malleable iron Farm and construction machinery, heavy-duty G D G
bearings, railroad rolling stock
Nickel Gas turbine blades, pump and valve F F F
components for chemical plants
Steel (carbon Die blocks, heavy-duty gear blanks, aircraft F E F
and low-alloy) undercarriage members, railroad wheels
Steel (high-alloy) Gas-turbine housings, pump and valve F E F
components, rock-Crusher jaws
White iron Mill liners, shot-blasting nozzles, railroad G VP VP
brake shoes, crushers, and pulverizers
Zinc Door handles, radiator grills E D E
“E = excellent; G 1 good; F = fair; VP I very poor; D = difficult.
TABLE l2.3
Properties and Typical Applications of Cast irons
Ultimate tensile Elongation
strength Yield strength in 50 mm
Cast iron Type (MPa) (MPa) (%) Typical applications
Gray Ferritic 170 140 0.4 Pipe, sanitary ware
Pearlitic 275 240 0.4 Engine blocks, machine tools
Martensitic 550 5 5 0 0 Wear surfaces
Ductile (Nodular) Ferritic 415 275 18 Pipe, general service
Pearlitic 550 380 6 Crankshafts, highly stressed
parts
Tempered martensite 825 620 2 High-strength machine parts,
wear-resistant parts
Malleable Ferritic 365 240 18 Hardware, pipe fittings,
general engineering service
Pearlitic 450 310 10 Railroad equipment,
couplings
Tempered martensite 700 550 2 Railroad equipment, gears,
connecting rods
White Pearlitic 275 275 0 Wear-resistant parts, mill
rolls
be used with them (Section 4.9). These alloys have high electrical conductivity and
generally good atmospheric corrosion resistance. However, their resistance to some
acids and all alkalis is poor, and care must be taken to prevent galvanic corrosion.
They are nontoxic, lightweight, and have good machinability. Except for alloys with
silicon, they generally have low resistance to wear and abrasion. Aluminum-based
alloys have numerous applications, including architectural and decorative uses. An
increasing trend is their use in automobiles, for components such as engine blocks,
cylinder heads, intake manifolds, transmission cases, suspension components, wheels