Page 271 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 271
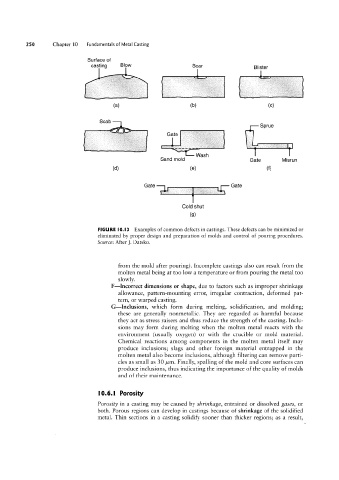
250 Chapter 10 Fundamentals of Metal Casting
Surface of
casting Blow Scar Buster
(D) (C)
(H)
Scab _g g Sprue
Wash
Sand mold Gate Misrun
(dl (G) (f)
Gate Gate
Cold shut
(9)
FIGURE l0.I3 Examples of common defects in castings. These defects can be minimized or
eliminated by proper design and preparation of molds and control of pouring procedures.
Source: After ]. Datsko.
from the mold after pouring). Incomplete castings also can result from the
molten metal being at too low a temperature or from pouring the metal too
slowly.
F-Incorrect dimensions or shape, due to factors such as improper shrinkage
allowance, pattern-mounting error, irregular contraction, deformed pat-
tern, or Warped casting.
G-Inclusions, Which form during melting, solidification, and molding;
these are generally nonmetallic. They are regarded as harmful because
they act as stress raisers and thus reduce the strength of the casting. Inclu-
sions may form during melting when the molten metal reacts with the
environment (usually oxygen) or with the Crucible or mold material.
Chemical reactions among components in the molten metal itself may
produce inclusions; slags and other foreign material entrapped in the
molten metal also become inclusions, although filtering can remove parti-
cles as small as 30 um. Finally, spalling of the mold and core surfaces can
produce inclusions, thus indicating the importance of the quality of molds
and of their maintenance.
l0.6.l Porosity
Porosity in a casting may be caused by shrinkage, entrained or dissolved gases, or
both. Porous regions can develop in castings because of shrinkage of the solidified
metal. Thin sections in a casting solidify sooner than thicker regions; as a result,