Page 274 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 274
Summary 253
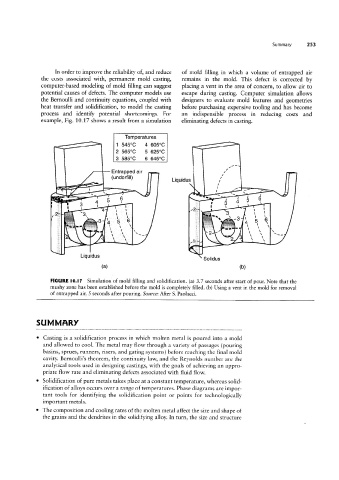
In order to improve the reliability of, and reduce of mold filling in which a volume of entrapped air
the costs associated with, permanent mold casting, remains in the mold. This defect is corrected by
computer-based modeling of mold filling can suggest placing a vent in the area of concern, to allow air to
potential causes of defects. The computer models use escape during casting. Computer simulation allows
the Bernoulli and continuity equations, coupled with designers to evaluate mold features and geometries
heat transfer and solidification, to model the casting before purchasing expensive tooling and has become
process and identify potential shortcomings. For an indispensible process in reducing costs and
example, Fig. 10.17 shows a result from a simulation eliminating defects in casting.
Temperatures
/-" ' 1 545°c 4 so5°C /'
2 565°C 5 625°C A
3 585°C 6 645°C
T9; Entrapped air Liquidus
(underfill)
ei* I ` ` __ ~`, `~ " 1' _» 5
/
\ -" "T/T 4 Q I é
E;
,221 | 3 \ I I \
.E
‘,
if 1 ‘4 \ 1 3 \ \
3 4 5 6 4 Q \
,it _- 35, .\ -\ \ \\ \ \
H _ \ \ \\ ` \ 3; \ 2_ / ‘ si \ \ \\ \ \ `'
~¢.. -»-»» \ ‘f¢~~ 1. ` \ \
'QI
L'q“‘d“S sondus
(H) (D)
FIGURE l0.l7 Simulation of mold filling and solidification. (a) 3.7 seconds after start of pour. Note that the
mushy zone has been established before the mold is completely filled. (b) Using a vent in the mold for removal
of entrapped air, 5 seconds after pouring. Source: After S. Paolucci.
SUMMARY
Casting is a solidification process in which molten metal is poured into a mold
and allowed to cool. The metal may flow through a variety of passages (pouring
basins, sprues, runners, risers, and gating systems) before reaching the final mold
cavity. Bernoulli’s theorem, the continuity law, and the Reynolds number are the
analytical tools used in designing castings, with the goals of achieving an appro-
priate flow rate and eliminating defects associated with fluid flow.
Solidification of pure metals takes place at a constant temperature, whereas solid-
ification of alloys occurs over a range of temperatures. Phase diagrams are impor-
tant tools for identifying the solidification point or points for technologically
important metals.
The composition and cooling rates of the molten metal affect the size and shape of
the grains and the dendrites in the solidifying alloy. In turn, the size and structure