Page 459 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 459
Section 17.2 Production of Metal Powders
Pressing Coining
Atomization lsostatic pressing Forging
Reduction ROIHIWQ Machining
Electrolytic deposition Extrusion Atmosphere i-ieai treating
plféils comciniggtion Sintermg Secondary
Carbonyls lniection molding Vacuum impregnation
Comminution { Infiltration
Mechanical alloying I Piaiing
'
r
I
-
Hot a2s;i;if:;;@
Lubricants
lsostatid pressing
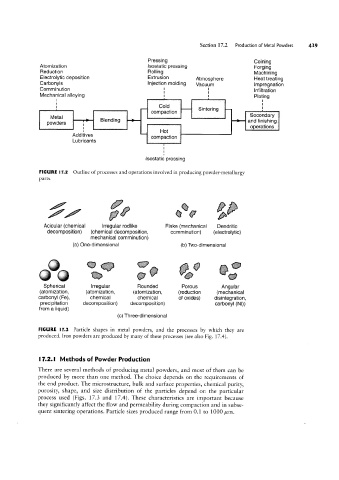
FIGURE l1.2 Outline of processes and operations involved in producing powder-metallurgy
parts.
` ”
Acicular (chemical Irregular rodlike Flake (mechanical Dendritic
decomposition) (chemical decomposition, Comminution) (electrolytic)
mechanical Comminution)
(a) One-dimensional (b) Two-dimensional
Spherical Irregular Rounded Porous Angular
(atomization, (atomization, (atomization, (reduction (mechanical
carbonyl (Fe) chemical chemical of oxides) disintegration
precipitation decomposition) decomposition) carbonyl (Ni)),
from a liquid)
(c) Three-dimensional
FIGURE l7.3 Particle shapes in metal powders, and the processes by which they are
produced. Iron powders are produced by many of these processes (see also Fig. 17.4).
l7.2.| Methods of Powder Production
There are several methods of producing metal powders, and most of them can be
produced by more than one method. The choice depends on the requirements of
the end product. The microstructure, bulk and surface properties, chemical purity,
porosity, shape, and size distribution of the particles depend on the particular
process used (Figs. 17.3 and 17.4). These characteristics are important because
they significantly affect the flow and permeability during compaction and in subse-
quent sintering operations. Particle sizes produced range from 0.1 to 1000 um.