Page 52 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 52
General Introduction
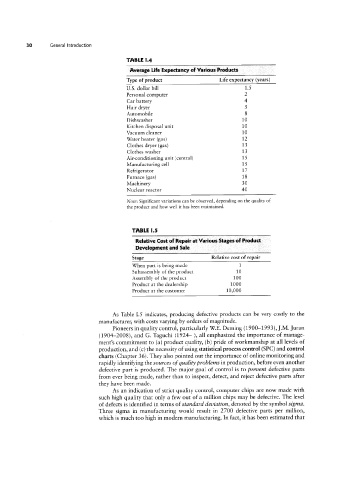
TABLE l.4
Average Life Expectancy of Various Products
Type of product Life expectancy (years)
U.S. dollar bill 1.5
Personal computer 2
Car battery 4
Hair dryer 5
Automobile 8
Dishwasher 10
Kitchen disposal unit 10
Vacuum cleaner 10
Water heater (gas) 12
Clothes dryer (gas) 13
Clothes washer 13
Air-conditioning unit (central) 15
Manufacturing cell 15
Refrigerator 17
Furnace (gas) 18
Machinery 30
Nuclear reactor 40
Note: Significant variations can be observed, depending on the quality of
the product and how well it has been maintained.
TABLE l.5
Relative Cost of Repair at Various Stages of Product
Development and Sale
Stage Relative cost of repair
When part is being made 1
Subassembly of the product 10
Assembly of the product 100
Product at the dealership 1000
Product at the customer 10,000
As Table L5 indicates, producing defective products can be very costly to the
manufacturer, with costs varying by orders of magnitude.
Pioneers in quality control, particularly \X/.E. Deming (1900-1993), ].M. ]uran
(1904-2008), and G. Taguchi (1924- ), all emphasized the importance of manage-
ment’s commitment to (a) product quality, (b) pride of workmanship at all levels of
production, and (c) the necessity of using statistical process control (SPC) and control
charts (Chapter 36). They also pointed out the importance of online monitoring and
rapidly identifying the sources ofquality problems in production, before even another
defective part is produced. The major goal of control is to prevent defective parts
from ever being made, rather than to inspect, detect, and reject defective parts after
they have been made.
As an indication of strict quality control, computer chips are now made with
such high quality that only a few out of a million chips may be defective. The level
of defects is identified in terms of standard deviation, denoted by the symbol sigma.
Three sigma in manufacturing would result in 2700 defective parts per million,
which is much too high in modern manufacturing. In fact, it has been estimated that