Page 652 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 652
Section 23.3 Lathes and Lathe Operations 633
tools and performs several operations on different surfaces of the workpiece
(Fig. 23.10b). Workpiece diameters may be as much as 1 m.
To take advantage of new cutting-tool materials, computer-controlled lathes
are designed to operate faster and have higher power available compared with other
lathes. They are equipped with automatic tool changers (ATCs). Their operations
are reliably repetitive, maintain the desired dimensional accuracy, and require less
skilled labor (once the machine is set up). They are suitable for low- to medium-
volume production.
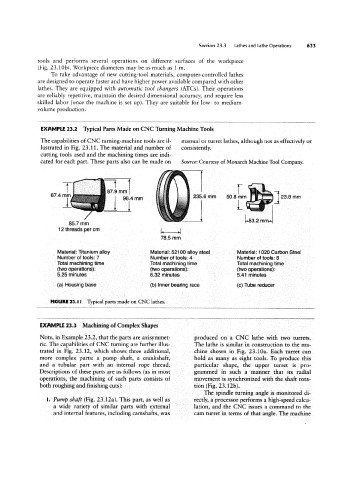
EXAMPLE 23.2 Typical Parts Made on CNC Turning Machine Tools
The capabilities of CNC turning-machine tools are il- manual or turret lathes, although not as effectively or
lustrated in Fig. 23.11. The material and number of consistently.
cutting tools used and the machining times are indi-
cated for each part. These parts also can be made on Source: Courtesy of Monarch Machine Tool Company.
is J
85.7 mm i‘53°2 m
12 threads per cm
78.5 mm
Material: Titanium alloy Material: 52100 alloy steel Material: 1020 Carbon Steel
Number of tools: 7 Number of tools: 4 Number of tools: 8
Total machining time Total machining time Total machining time
(two operations): (two operations): (two operations):
5.25 minutes 6.32 minutes 5.41 minutes
(a) Housing base (b) Inner bearing race (c) Tube reducer
HGURE 23.| I Typical parts made on CNC lathes.
EXAMPLE 23.3 Machining of Complex Shapes
Note, in Example 23.2, that the parts are axisymmet- produced on a CNC lathe with two turrets.
ric. The capabilities of CNC turning are further illus- The lathe is similar in construction to the ma-
trated in Fig. 23.12, which shows three additional, chine shown in Fig. 23.10a. Each turret can
more complex parts: a pump shaft, a crankshaft, hold as many as eight tools. To produce this
and a tubular part with an internal rope thread. particular shape, the upper turret is pro-
Descriptions of these parts are as follows (as in most grammed in such a manner that its radial
operations, the machining of such parts consists of movement is synchronized with the shaft rota-
both roughing and finishing cuts): tion (Fig. 23.12b).
The spindle turning angle is monitored di-
I. Pump shaft (Fig. 23.12a). This part, as Well as rectly, a processor performs a high-speed calcu-
a wide variety of similar parts with external lation, and the CNC issues a command to the
and internal features, including camshafts, was cam turret in terms of that angle. The machine