Page 114 - Marine Structural Design
P. 114
90 Part I Situcrural Design Principles
Loads (for Limit States (S) (or Safety factor
Structure strength criteria)
Design various loading yielding,
conditions)
buckling, fatigue
yes b stop
Structural
<
Response (R) YR .qX) qX) /YS
Redesign
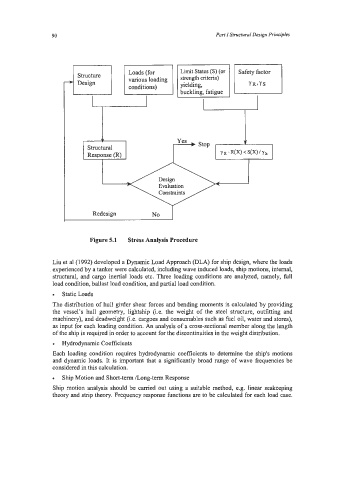
Figure 5.1 Stress Analysis Procedure
Liu et a1 (1992) developed a Dynamic Load Approach @LA) for ship design, where the loads
experienced by a tanker were calculated, including wave induced loads, ship motions, internal,
structural, and cargo inertial loads etc. Three loading conditions are analyzed, namely, full
load condition, ballast load condition, and partial load condition.
StaticLoads
The distribution of hull girder shear forces and bending moments is calculated by providing
the vessel's hull geometry, lightship (i.e. the weight of the steel structure, outfitting and
machinery), and deadweight (i.e. cargoes and consumables such as fuel oil, water and stores),
as input for each loading condition. An analysis of a cross-sectional member along the length
of the ship is required in order to account for the discontinuities in the weight distribution.
Hydrodynamic Coefficients
Each loading condition requires hydrodynamic coefficients to determine the ship's motions
and dynamic loads. It is important that a significantly broad range of wave frequencies be
considered in this calculation.
Ship Motion and Short-term /Long-term Response
Ship motion analysis should be carried out using a suitable method, e.g. linear seakeeping
theory and strip theory. Frequency response functions are to be calculated for each load case.