Page 337 - Marine Structural Design
P. 337
ChapterI5 Offshore Structures Under Earthquake Loads 313
Soil
- stiffnrsr x 1.0
Soil
--- siiffnrrs I 0.1
---- Soil stiffness rn 10
2100 -
3200 t
2'oo
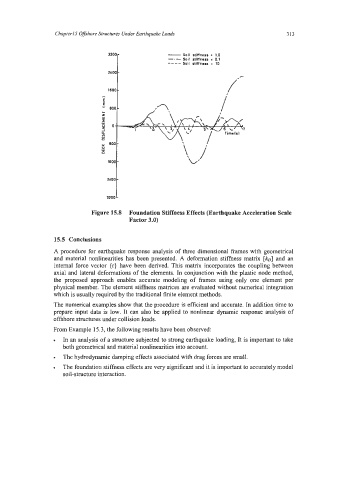
Figure 15.8 Foundation Stiffness Effects (Earthquake Acceleration Scale
Factor 3.0)
15.5 Conclusions
A procedure for earthquake response analysis of three dimensional frames with geometrical
and material nonlinearities has been presented. A deformation stiffness matrix [k~] and an
internal force vector {r} have been derived. This matrix incorporates the coupling between
axial and lateral deformations of the elements. In conjunction with the plastic node method,
the proposed approach enables accurate modeling of frames using only one element per
physical member. The element stiffness matrices are evaluated without numerical integration
which is usually required by the traditional finite element methods.
The numerical examples show that the procedure is efficient and accurate. In addition time to
prepare input data is low. It can also be applied to nonlinear dynamic response analysis of
offshore structures under collision loads.
From Example 15.3, the following results have been observed
In an analysis of a structure subjected to strong earthquake loading, It is important to take
both geometrical and material nonlinearities into account.
The hydrodynamic damping effects associated with drag forces are small.
The foundation stiffness effects are very significant and it is important to accurately model
soil-structure interaction.