Page 388 - Marine Structural Design
P. 388
364 Part III Fatigue and Fracture
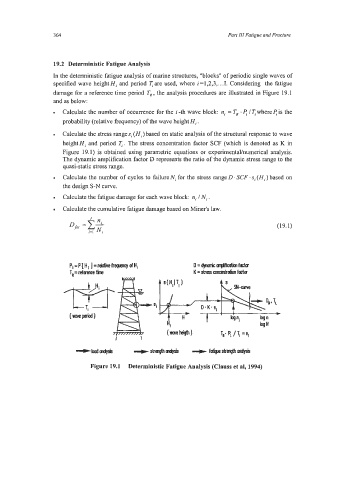
19.2 Deterministic Fatigue Analysis
In the deterministic fatigue analysis of marine structures, "blocks" of periodic single waves of
specified wave height Hi and period are used, where i =1,2,3,. . .I. Considering the fatigue
damage for a reference time period TR , the analysis procedures are illustrated in Figure 19.1
and as below:
Calculate the number of occurrence for the i -th wave block: n, = T, e< I I;. where < is the
probability (relative frequency) of the wave height Hi.
Calculate the stress ranges,(H,) based on static analysis of the structural response to wave
height Hi and period Ti. The stress concentration factor SCF (which is denoted as K in
Figure 19.1) is obtained using parametric equations or experimentallnumerical analysis.
The dynamic amplification factor D represents the ratio of the dynamic stress range to the
quasi-static stress range.
Calculate the number of cycles to failure N, for the stress range De SCF .si (Hi) based on
the design S-N curve.
Calculate the fatigue damage for each wave block: n, / Ni .
Calculate the cumulative fatigue damage based on Miner's law.
(19.1)
Figure 19.1 Deterministic Fatigue Analysis (Clauss et al, 1994)