Page 453 - Marine Structural Design
P. 453
Chapter 23 Basics of Structural Reliabilily 429
R=20*U1+150
S=30*U2+90
Then, the limit state function can be reformed as
G(Z)=20U1-30U2+60
The distance of the straight line from the origin of coordinates can be quickly
calculated as
60
p = JW 1.664
=
Using the standard normal distribution table (Table 23.1), the probability of failure
can be estimated as
P, = O(- p) = O(- 1.664) = 4.9%
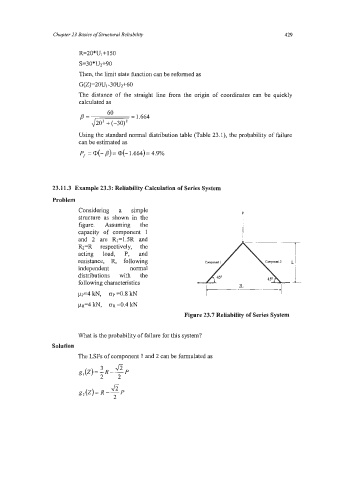
23.11.3 Example 23.3: Reliability Calculation of Series System
Problem
Considering a simple P
structure as shown in the
figure. Assuming the
capacity of component 1
and 2 are Rl=lSR and
Rz=R respectively, the
acting load, P, and
resistance, R, following
independent normal
distributions with the
following characteristics
pp’4 kN, ~p =0.8 kN
p~=4 kN, GR ~0.4 kN
Figure 23.7 Reliability of Series System
What is the probability of failure for this system?
Solution
The LSFs of component 1 and 2 can be formulated as
4
5
3
g, (2) = --R - -
P
2 2
Jz
g, (2) = R - --P
2