Page 216 - Marketing Management
P. 216
ANALYZING BUSINESS MARKETS | CHAPTER 7 193
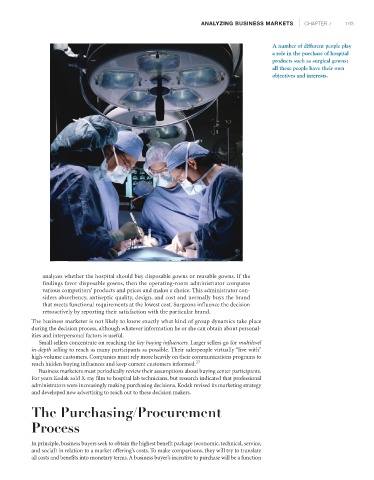
A number of different people play
a role in the purchase of hospital
products such as surgical gowns;
all these people have their own
objectives and interests.
analyzes whether the hospital should buy disposable gowns or reusable gowns. If the
findings favor disposable gowns, then the operating-room administrator compares
various competitors’ products and prices and makes a choice. This administrator con-
siders absorbency, antiseptic quality, design, and cost and normally buys the brand
that meets functional requirements at the lowest cost. Surgeons influence the decision
retroactively by reporting their satisfaction with the particular brand.
The business marketer is not likely to know exactly what kind of group dynamics take place
during the decision process, although whatever information he or she can obtain about personal-
ities and interpersonal factors is useful.
Small sellers concentrate on reaching the key buying influencers. Larger sellers go for multilevel
in-depth selling to reach as many participants as possible. Their salespeople virtually “live with”
high-volume customers. Companies must rely more heavily on their communications programs to
reach hidden buying influences and keep current customers informed. 27
Business marketers must periodically review their assumptions about buying center participants.
For years Kodak sold X-ray film to hospital lab technicians, but research indicated that professional
administrators were increasingly making purchasing decisions. Kodak revised its marketing strategy
and developed new advertising to reach out to these decision makers.
The Purchasing/Procurement
Process
In principle, business buyers seek to obtain the highest benefit package (economic, technical, service,
and social) in relation to a market offering’s costs. To make comparisons, they will try to translate
all costs and benefits into monetary terms. A business buyer’s incentive to purchase will be a function