Page 387 - Marketing Management
P. 387
364 PART 5 SHAPING THE MARKET OFFERINGS
wrongs. Unfortunately, although many firms have well-designed and executed procedures to deal
with their own failures, they find managing customer failures—when a service problem arises from
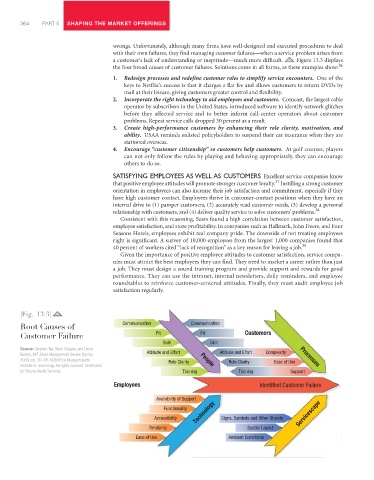
a customer’s lack of understanding or ineptitude—much more difficult. Figure 13.3 displays
the four broad causes of customer failures. Solutions come in all forms, as these examples show: 36
1. Redesign processes and redefine customer roles to simplify service encounters. One of the
keys to Netflix’s success is that it charges a flat fee and allows customers to return DVDs by
mail at their leisure, giving customers greater control and flexibility.
2. Incorporate the right technology to aid employees and customers. Comcast, the largest cable
operator by subscribers in the United States, introduced software to identify network glitches
before they affected service and to better inform call-center operators about customer
problems. Repeat service calls dropped 30 percent as a result.
3. Create high-performance customers by enhancing their role clarity, motivation, and
ability. USAA reminds enlisted policyholders to suspend their car insurance when they are
stationed overseas.
4. Encourage “customer citizenship” so customers help customers. At golf courses, players
can not only follow the rules by playing and behaving appropriately, they can encourage
others to do so.
SATISFYING EMPLOYEES AS WELL AS CUSTOMERS Excellent service companies know
37
that positive employee attitudes will promote stronger customer loyalty. Instilling a strong customer
orientation in employees can also increase their job satisfaction and commitment, especially if they
have high customer contact. Employees thrive in customer-contact positions when they have an
internal drive to (1) pamper customers, (2) accurately read customer needs, (3) develop a personal
relationship with customers, and (4) deliver quality service to solve customers’ problems. 38
Consistent with this reasoning, Sears found a high correlation between customer satisfaction,
employee satisfaction, and store profitability. In companies such as Hallmark, John Deere, and Four
Seasons Hotels, employees exhibit real company pride. The downside of not treating employees
right is significant. A survey of 10,000 employees from the largest 1,000 companies found that
40 percent of workers cited “lack of recognition” as a key reason for leaving a job. 39
Given the importance of positive employee attitudes to customer satisfaction, service compa-
nies must attract the best employees they can find. They need to market a career rather than just
a job. They must design a sound training program and provide support and rewards for good
performance. They can use the intranet, internal newsletters, daily reminders, and employee
roundtables to reinforce customer-centered attitudes. Finally, they must audit employee job
satisfaction regularly.
|Fig. 13.3|
Root Causes of Communication Communication
Customer Failure Fit Fit Customers
Skill Skill
Source: Stephen Tax, Mark Colgate, and David
Attitude and Effort Attitude and Effort Complexity
Bowen, MIT Sloan Management Review (Spring
2006): pp. 30–38. ©2006 by Massachusetts Role Clarity People Role Clarity Ease of Use Processes
Institute of Technology. All rights reserved. Distributed
by Tribune Media Services. Training Training Support
Employees Identified Customer Failure
Availability of Support
Technology Servicescape
Functionality
Accessibility Signs, Symbols and Other Objects
Reliability Spatial Layout
Ease of Use Ambient Conditions