Page 396 - Marketing Management
P. 396
DESIGNING AND MANAGING SERVICES | CHAPTER 13 373
which top service marketing organizations can adhere. Two important considerations in service
delivery are managing customer expectations and incorporating self-service technologies.
Managing Customer Expectations
Customers form service expectations from many sources, such as past experiences, word of mouth,
67
and advertising. In general, customers compare the perceived service with the expected service. If
the perceived service falls below the expected service, customers are disappointed. Successful com-
panies add benefits to their offering that not only satisfy customers but surprise and delight them.
Delighting customers is a matter of exceeding expectations. 68
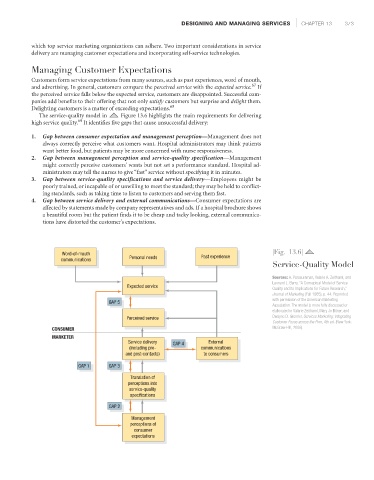
The service-quality model in Figure 13.6 highlights the main requirements for delivering
69
high service quality. It identifies five gaps that cause unsuccessful delivery:
1. Gap between consumer expectation and management perception—Management does not
always correctly perceive what customers want. Hospital administrators may think patients
want better food, but patients may be more concerned with nurse responsiveness.
2. Gap between management perception and service-quality specification—Management
might correctly perceive customers’ wants but not set a performance standard. Hospital ad-
ministrators may tell the nurses to give “fast” service without specifying it in minutes.
3. Gap between service-quality specifications and service delivery—Employees might be
poorly trained, or incapable of or unwilling to meet the standard; they may be held to conflict-
ing standards, such as taking time to listen to customers and serving them fast.
4. Gap between service delivery and external communications—Consumer expectations are
affected by statements made by company representatives and ads. If a hospital brochure shows
a beautiful room but the patient finds it to be cheap and tacky looking, external communica-
tions have distorted the customer’s expectations.
Word-of-mouth |Fig. 13.6|
communications Personal needs Past experience
Service-Quality Model
Sources: A. Parasuraman, Valarie A. Zeithaml, and
Leonard L. Berry, “A Conceptual Model of Service
Expected service
Quality and Its Implications for Future Research,”
Journal of Marketing (Fall 1985), p. 44. Reprinted
with permission of the American Marketing
GAP 5
Association. The model is more fully discussed or
elaborated in Valarie Zeithaml, Mary Jo Bitner, and
Perceived service Dwayne D. Gremler, Services Marketing: Integrating
Customer Focus across the Firm, 4th ed. (New York:
CONSUMER McGraw-Hill, 2006).
MARKETER
Service delivery GAP 4 External
(including pre- communications
and post-contacts) to consumers
GAP 1 GAP 3
Translation of
perceptions into
service-quality
specifications
GAP 2
Management
perceptions of
consumer
expectations