Page 263 - Master Handbook of Acoustics
P. 263
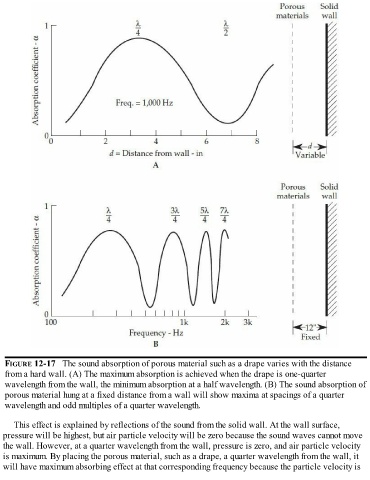
FIGURE 12-17 The sound absorption of porous material such as a drape varies with the distance
from a hard wall. (A) The maximum absorption is achieved when the drape is one-quarter
wavelength from the wall, the minimum absorption at a half wavelength. (B) The sound absorption of
porous material hung at a fixed distance from a wall will show maxima at spacings of a quarter
wavelength and odd multiples of a quarter wavelength.
This effect is explained by reflections of the sound from the solid wall. At the wall surface,
pressure will be highest, but air particle velocity will be zero because the sound waves cannot move
the wall. However, at a quarter wavelength from the wall, pressure is zero, and air particle velocity
is maximum. By placing the porous material, such as a drape, a quarter wavelength from the wall, it
will have maximum absorbing effect at that corresponding frequency because the particle velocity is