Page 32 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 32
19
2.2. Types of Bonding in Solids
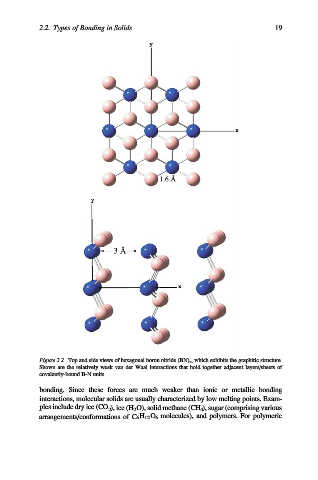
Figure 2.2. Top and side views of hexagonal boron nitride (BN) x , which exhibits the graphitic structure.
Shown are the relatively weak van der Waal interactions that hold together adjacent layers/sheets of
covalently-bound B-N units.
bonding. Since these forces are much weaker than ionic or metallic bonding
interactions, molecular solids are usually characterized by low melting points. Exam-
ples include dry ice (CO 2 ), ice (H 2 O), solid methane (CH 4 ), sugar (comprising various
arrangements/conformations of C 6 H 12 O 6 molecules), and polymers. For polymeric