Page 69 - Mathematical Models and Algorithms for Power System Optimization
P. 69
Optimization of Annual Generator Maintenance Scheduling 59
3.4 Fuzzification of GMS Model
3.4.1 Selection of Fuzzy Membership Function
Fuzzy membership function is a proper mathematical description for the “subject” to make
subjective evaluation of the “object.” However, different “subjects” may have different
evaluations of the “object,” and hence it is required to employ different fuzzy membership
functions to describe them.
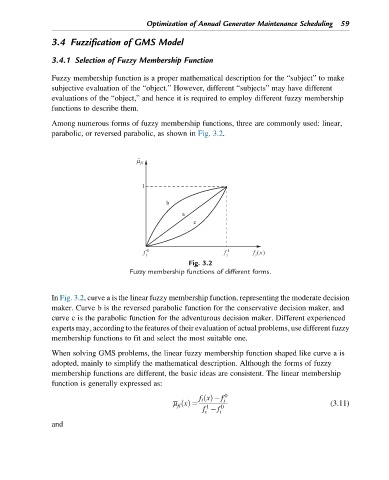
Among numerous forms of fuzzy membership functions, three are commonly used: linear,
parabolic, or reversed parabolic, as shown in Fig. 3.2.
Fig. 3.2
Fuzzy membership functions of different forms.
In Fig. 3.2, curve a is the linear fuzzy membership function, representing the moderate decision
maker. Curve b is the reversed parabolic function for the conservative decision maker, and
curve c is the parabolic function for the adventurous decision maker. Different experienced
experts may, according to the features of their evaluation of actual problems, use different fuzzy
membership functions to fit and select the most suitable one.
When solving GMS problems, the linear fuzzy membership function shaped like curve a is
adopted, mainly to simplify the mathematical description. Although the forms of fuzzy
membership functions are different, the basic ideas are consistent. The linear membership
function is generally expressed as:
f i xðÞ f i 0
μ xðÞ ¼ (3.11)
fi
1
f f i 0
i
and