Page 118 - Mathematical Techniques of Fractional Order Systems
P. 118
106 Mathematical Techniques of Fractional Order Systems
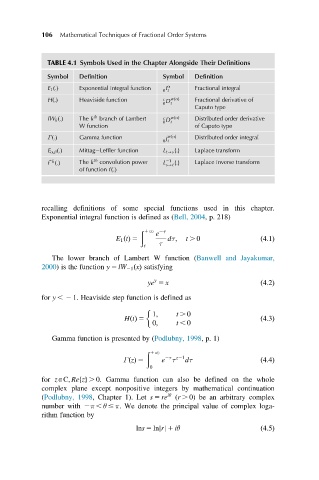
TABLE 4.1 Symbols Used in the Chapter Alongside Their Definitions
Symbol Definition Symbol Definition
α
E 1 :ðÞ Exponential integral function 0 t I Fractional integral
H :ðÞ Heaviside function c wðαÞ Fractional derivative of
0 D t
Caputo type
lW k :ðÞ The k th branch of Lambert c wðαÞ Distributed order derivative
0 D t
W function of Caputo type
Γ :ðÞ Gamma function J wðαÞ Distributed order integral
0 t
E α;β :ðÞ Mittag Leffler function L t-s :fg Laplace transform
k The k th convolution power 21 Laplace inverse transform
f ðÞ : L s-t : fg
of function f :ðÞ
recalling definitions of some special functions used in this chapter.
Exponential integral function is defined as (Bell, 2004, p. 218)
1N 2τ
ð e
E 1 tðÞ 5 dτ; t . 0 ð4:1Þ
t τ
The lower branch of Lambert W function (Banwell and Jayakumar,
2000) is the function y 5 lW 21 xðÞ satisfying
y
ye 5 x ð4:2Þ
for y ,2 1. Heaviside step function is defined as
1; t . 0
HtðÞ 5 ð4:3Þ
0; t , 0
Gamma function is presented by (Podlubny, 1998,p. 1)
ð 1N
2τ z21
Γ zðÞ 5 e τ dτ ð4:4Þ
0
for zAC; Re zfg . 0. Gamma function can also be defined on the whole
complex plane except nonpositive integers by mathematical continuation
iθ
(Podlubny, 1998, Chapter 1). Let s 5 re (r . 0) be an arbitrary complex
number with 2π , θ # π. We denote the principal value of complex loga-
rithm function by
lns 5 ln r jj 1 iθ ð4:5Þ