Page 13 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 13
2 MECHANICAL ENGINEER’S DATA HANDBOOK
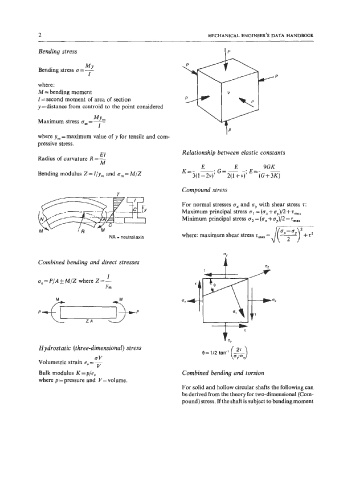
Bending stress
MY
Bending stress a = -
I P
where:
M = bending moment V
I = second moment of area of section
y = distance from centroid to the point considered
MYm
Maximum stress am=-
I
where y, =maximum value of y for tensile and com-
pressive stress.
El Relationship between elastic constants
Radius of curvature R = -
M
Bending modulus Z = I/ym and u,,, = M/Z
Compound stress
T
For normal stresses u, and ay with shear stress 5:
Maximum principal stress a1 = (a, + ay)/2 +
Minimum principal stress a2 = (a, + aJ2 -t,,,
NA = neutral axis
Combined bending and direct stresses
I
a, = PIA M/Z where Z = -
Ylll
e= 112 tan-‘ (+I
Hydrostatic (three-dimensional) stress
UV
Volumetric strain e, = -
V
Bulk modulus K =pie, Combined bending and torsion
where p = pressure and V= volume.
For solid and hollow circular shafts the following can
be derived from the theory for two-dimensional (Com-
pound) stress. If the shaft is subject to bending moment