Page 16 - Mechanical Engineer's Data Handbook
P. 16
STRENGTHS OF MATERIALS 5
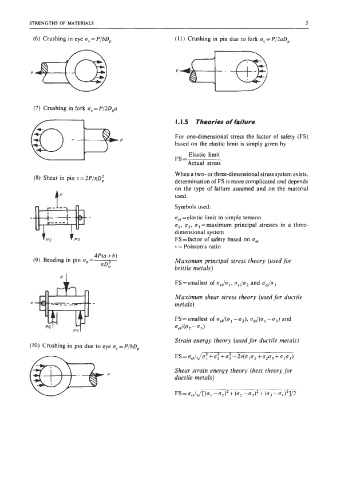
(6) Crushing in eye a, = P/bD, (1 1) Crushing in pin due to fork a, = P/2aD,
p E @
(7) Crushing in fork uc = P/2Dpa
I. I .5 Theories of failure
@T+-jLp
For one-dimensional stress the factor of safety (FS)
based on the elastic limit is simply given by
Elastic limit
FS =
Actual stress‘
When a two- or three-dimensional stress system exists,
(8) Shear in pin r=2P/7rD; determination of FS is more complicated and depends
sp on the type of failure assumed and on the material
used.
Symbols used:
ael =elastic limit in simple tension
at, az, a,=maximum principal stresses in a three-
dimensional system
tPl2 i Pi2 FS = factor of safety based on a,,
v = Poisson’s ratio
4P(a + b)
(9) Bending in pin ab=- Maximum principal stress theory (used for
ZDP”
brittle metals)
PI
FS =smallest of ael/uI, aeJa2 and ael/a3
Maximum shear stress theory (used for ductile
metals)
FS = smallest of ae,/(ul -a2), aeI/(aI - a3) and
a,,/(a, -03)
Strain energy theory (used for ductile metals)
(10) Crushing in pin due to eye a, = P/bDp
n FS = a,,/Ja: + a: + a: - 2v(alaz +a2a, + a,a3)
Shear strain energy theory (best theory for
ductile metals)
W