Page 180 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 2)
P. 180
5 Optical Methods 169
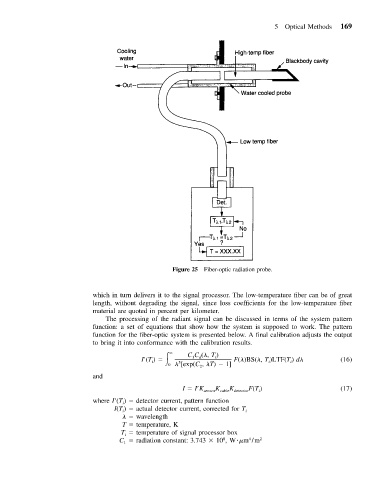
Figure 25 Fiber-optic radiation probe.
which in turn delivers it to the signal processor. The low-temperature fiber can be of great
length, without degrading the signal, since loss coefficients for the low-temperature fiber
material are quoted in percent per kilometer.
The processing of the radiant signal can be discussed in terms of the system pattern
function: a set of equations that show how the system is supposed to work. The pattern
function for the fiber-optic system is presented below. A final calibration adjusts the output
to bring it into conformance with the calibration results.
I (T ) CC (
, T )
1
i
d
i
i
i
0
[exp(C ,
T) 1] F(
)BS(
, T )LTF(T ) d
(16)
5
2
and
I I K sensor K cable K detector F(T ) (17)
i
where I (T ) detector current, pattern function
i
I(T ) actual detector current, corrected for T i
i
wavelength
T temperature, K
T temperature of signal processor box
i
C radiation constant: 3.743 10 ,W m /m 2
8
4
1