Page 381 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 2)
P. 381
372 Mathematical Models of Dynamic Physical Systems
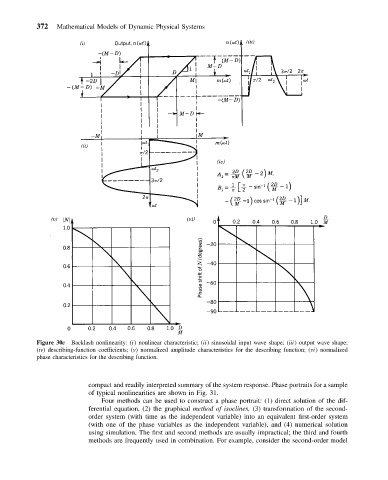
Figure 30c Backlash nonlinearity: (i) nonlinear characteristic; (ii) sinusoidal input wave shape; (iii) output wave shape;
(iv) describing-function coefficients; (v) normalized amplitude characteristics for the describing function; (vi) normalized
phase characteristics for the describing function.
compact and readily interpreted summary of the system response. Phase portraits for a sample
of typical nonlinearities are shown in Fig. 31.
Four methods can be used to construct a phase portrait: (1) direct solution of the dif-
ferential equation, (2) the graphical method of isoclines, (3) transformation of the second-
order system (with time as the independent variable) into an equivalent first-order system
(with one of the phase variables as the independent variable), and (4) numerical solution
using simulation. The first and second methods are usually impractical; the third and fourth
methods are frequently used in combination. For example, consider the second-order model