Page 161 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 161
150 Heat-Transfer Fundamentals
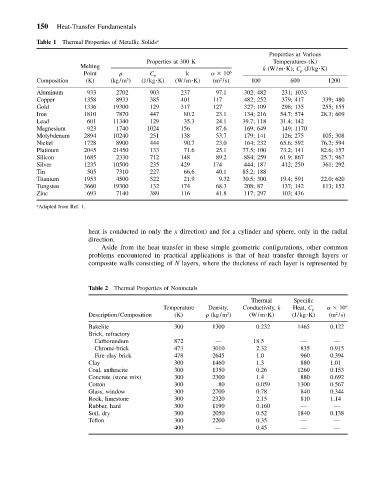
Table 1 Thermal Properties of Metallic Solids a
Properties at Various
Properties at 300 K Temperatures (K)
Melting k (W/m K); C p (J/kg K)
Point C p k 10 6
3
2
Composition (K) (kg/m ) (J/kg K) (W/m K) (m /s) 100 600 1200
Aluminum 933 2702 903 237 97.1 302; 482 231; 1033
Copper 1358 8933 385 401 117 482; 252 379; 417 339; 480
Gold 1336 19300 129 317 127 327; 109 298; 135 255; 155
Iron 1810 7870 447 80.2 23.1 134; 216 54.7; 574 28.3; 609
Lead 601 11340 129 35.3 24.1 39.7; 118 31.4; 142
Magnesium 923 1740 1024 156 87.6 169; 649 149; 1170
Molybdenum 2894 10240 251 138 53.7 179; 141 126; 275 105; 308
Nickel 1728 8900 444 90.7 23.0 164; 232 65.6; 592 76.2; 594
Platinum 2045 21450 133 71.6 25.1 77.5; 100 73.2; 141 82.6; 157
Silicon 1685 2330 712 148 89.2 884; 259 61.9; 867 25.7; 967
Silver 1235 10500 235 429 174 444; 187 412; 250 361; 292
Tin 505 7310 227 66.6 40.1 85.2; 188
Titanium 1953 4500 522 21.9 9.32 30.5; 300 19.4; 591 22.0; 620
Tungsten 3660 19300 132 174 68.3 208; 87 137; 142 113; 152
Zinc 693 7140 389 116 41.8 117; 297 103; 436
a
Adapted from Ref. 1.
heat is conducted in only the x direction) and for a cylinder and sphere, only in the radial
direction.
Aside from the heat transfer in these simple geometric configurations, other common
problems encountered in practical applications is that of heat transfer through layers or
composite walls consisting of N layers, where the thickness of each layer is represented by
Table 2 Thermal Properties of Nonmetals
Thermal Specific
Temperature Density, Conductivity, k Heat, C p 10 6
3
2
Description/Composition (K) (kg/m ) (W/m K) (J/kg K) (m /s)
Bakelite 300 1300 0.232 1465 0.122
Brick, refractory
Carborundum 872 — 18.5 — —
Chrome-brick 473 3010 2.32 835 0.915
Fire clay brick 478 2645 1.0 960 0.394
Clay 300 1460 1.3 880 1.01
Coal, anthracite 300 1350 0.26 1260 0.153
Concrete (stone mix) 300 2300 1.4 880 0.692
Cotton 300 80 0.059 1300 0.567
Glass, window 300 2700 0.78 840 0.344
Rock, limestone 300 2320 2.15 810 1.14
Rubber, hard 300 1190 0.160 — —
Soil, dry 300 2050 0.52 1840 0.138
Teflon 300 2200 0.35 — —
400 — 0.45 — —