Page 163 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 163
152 Heat-Transfer Fundamentals
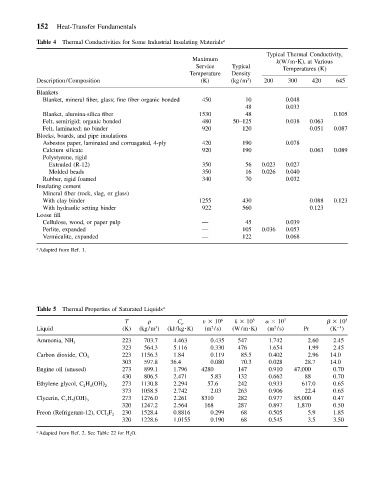
Table 4 Thermal Conductivities for Some Industrial Insulating Materials a
Typical Thermal Conductivity,
Maximum k(W/m K), at Various
Service Typical Temperatures (K)
Temperature Density
3
Description/Composition (K) (kg/m ) 200 300 420 645
Blankets
Blanket, mineral fiber, glass; fine fiber organic bonded 450 10 0.048
48 0.033
Blanket, alumina-silica fiber 1530 48 0.105
Felt, semirigid; organic bonded 480 50–125 0.038 0.063
Felt, laminated; no binder 920 120 0.051 0.087
Blocks, boards, and pipe insulations
Asbestos paper, laminated and corruagated, 4-ply 420 190 0.078
Calcium silicate 920 190 0.063 0.089
Polystyrene, rigid
Extruded (R-12) 350 56 0.023 0.027
Molded beads 350 16 0.026 0.040
Rubber, rigid foamed 340 70 0.032
Insulating cement
Mineral fiber (rock, slag, or glass)
With clay binder 1255 430 0.088 0.123
With hydraulic setting binder 922 560 0.123
Loose fill
Cellulose, wood, or paper pulp — 45 0.039
Perlite, expanded — 105 0.036 0.053
Vermiculite, expanded — 122 0.068
a
Adapted from Ref. 1.
Table 5 Thermal Properties of Saturated Liquids a
T C p v 10 6 k 10 3 10 7 10 3
3
2
1
2
Liquid (K) (kg/m ) (kJ/kg K) (m /s) (W/m K) (m /s) Pr (K )
223 703.7 4.463 0.435 547 1.742 2.60 2.45
Ammonia, NH 3
323 564.3 5.116 0.330 476 1.654 1.99 2.45
223 1156.3 1.84 0.119 85.5 0.402 2.96 14.0
Carbon dioxide, CO 2
303 597.8 36.4 0.080 70.3 0.028 28.7 14.0
Engine oil (unused) 273 899.1 1.796 4280 147 0.910 47,000 0.70
430 806.5 2.471 5.83 132 0.662 88 0.70
273 1130.8 2.294 57.6 242 0.933 617.0 0.65
Ethylene glycol, C 2 H 4 (OH) 2
373 1058.5 2.742 2.03 263 0.906 22.4 0.65
273 1276.0 2.261 8310 282 0.977 85,000 0.47
Clycerin, C 3 H 5 (OH) 3
320 1247.2 2.564 168 287 0.897 1,870 0.50
230 1528.4 0.8816 0.299 68 0.505 5.9 1.85
Freon (Refrigerant-12), CCI 2 F 2
320 1228.6 1.0155 0.190 68 0.545 3.5 3.50
a
Adapted from Ref. 2. See Table 22 for H 2 O.