Page 167 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 167
156 Heat-Transfer Fundamentals
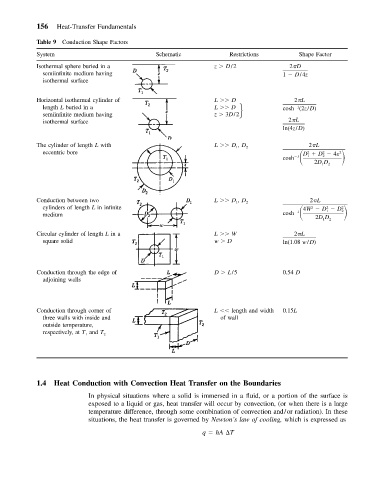
Table 9 Conduction Shape Factors
System Schematic Restrictions Shape Factor
Isothermal sphere buried in a z D/2 2 D
semiinfinite medium having 1 D/4z
isothermal surface
Horizontal isothermal cylinder of L D 2 L
length L buried in a L D cosh (2z/D)
1
semiinfinite medium having z 3D/2
isothermal surface 2 L
ln(4z/D)
The cylinder of length L with L D 1 , D 2 2 L
eccentric bore cosh D D 4 2
2
2
2
1
1
2DD 2
1
Conduction between two L D 1 , D 2 2 L
cylinders of length L in infinite cosh 4W D D 2 2
2
2
1
medium 1
1
2DD 2
Circular cylinder of length L in a L W 2 L
square solid w D ln(1.08 w/D)
Conduction through the edge of D L/5 0.54 D
adjoining walls
Conduction through corner of L length and width 0.15L
three walls with inside and of wall
outside temperature,
respectively, at T 1 and T 2
1.4 Heat Conduction with Convection Heat Transfer on the Boundaries
In physical situations where a solid is immersed in a fluid, or a portion of the surface is
exposed to a liquid or gas, heat transfer will occur by convection, (or when there is a large
temperature difference, through some combination of convection and/or radiation). In these
situations, the heat transfer is governed by Newton’s law of cooling, which is expressed as
q hA T