Page 446 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 446
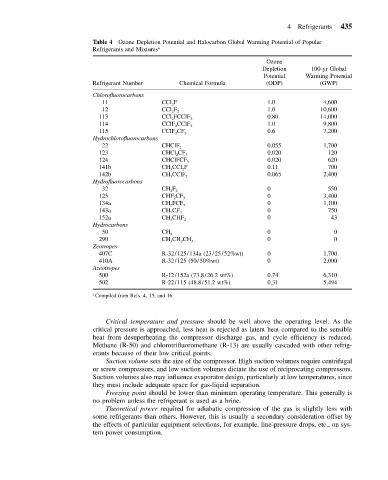
4 Refrigerants 435
Table 4 Ozone Depletion Potential and Halocarbon Global Warming Potential of Popular
Refrigerants and Mixtures a
Ozone
Depletion 100-yr Global
Potential Warming Potential
Refrigerant Number Chemical Formula (ODP) (GWP)
Chlorofluorocarbons
11 CCl 3 F 1.0 4,600
12 CCl 2 F 2 1.0 10,600
113 CCl 2 FCClF 2 0.80 14,000
114 CClF 2 CClF 2 1.0 9,800
115 CClF 2 CF 3 0.6 7,200
Hydrochlorofluorocarbons
22 CHClF 2 0.055 1,700
123 CHCl 2 CF 3 0.020 120
124 CHClFCF 3 0.020 620
141b CH 3 CCl 2 F 0.11 700
142b CH 3 CClF 2 0.065 2,400
Hydrofluorocarbons
32 CH 2 F 2 0 550
125 CHF 2 CF 3 0 3,400
134a CH 2 FCF 3 0 1,100
143a CH 3 CF 3 0 750
152a CH 3 CHF 2 0 43
Hydrocarbons
50 CH 4 0 0
290 CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 0 0
Zeotropes
407C R-32/125/134a (23/25/52%wt) 0 1,700
410A R-32/125 (50/50%wt) 0 2,000
Azeotropes
500 R-12/152a (73.8/26.2 wt%) 0.74 6,310
502 R-22/115 (48.8/51.2 wt%) 0.31 5,494
a Compiled from Refs. 4, 15, and 16.
Critical temperature and pressure should be well above the operating level. As the
critical pressure is approached, less heat is rejected as latent heat compared to the sensible
heat from desuperheating the compressor discharge gas, and cycle efficiency is reduced.
Methane (R-50) and chlorotrifluoromethane (R-13) are usually cascaded with other refrig-
erants because of their low critical points.
Suction volume sets the size of the compressor. High suction volumes require centrifugal
or screw compressors, and low suction volumes dictate the use of reciprocating compressors.
Suction volumes also may influence evaporator design, particularly at low temperatures, since
they must include adequate space for gas-liquid separation.
Freezing point should be lower than minimum operating temperature. This generally is
no problem unless the refrigerant is used as a brine.
Theoretical power required for adiabatic compression of the gas is slightly less with
some refrigerants than others. However, this is usually a secondary consideration offset by
the effects of particular equipment selections, for example, line-pressure drops, etc., on sys-
tem power consumption.