Page 553 - Mechanical Engineers' Handbook (Volume 4)
P. 553
542 Indoor Environmental Control
latent and sensible heat transfer for an occupant as would the actual environment (ANSI/
ASHRAE Standard 55-1992).
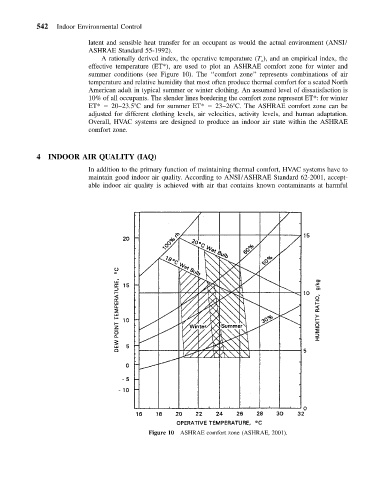
A rationally derived index, the operative temperature (T ), and an empirical index, the
o
effective temperature (ET*), are used to plot an ASHRAE comfort zone for winter and
summer conditions (see Figure 10). The ‘‘comfort zone’’ represents combinations of air
temperature and relative humidity that most often produce thermal comfort for a seated North
American adult in typical summer or winter clothing. An assumed level of dissatisfaction is
10% of all occupants. The slender lines bordering the comfort zone represent ET*: for winter
ET* 20–23.5 C and for summer ET* 23–26 C. The ASHRAE comfort zone can be
adjusted for different clothing levels, air velocities, activity levels, and human adaptation.
Overall, HVAC systems are designed to produce an indoor air state within the ASHRAE
comfort zone.
4 INDOOR AIR QUALITY (IAQ)
In addition to the primary function of maintaining thermal comfort, HVAC systems have to
maintain good indoor air quality. According to ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 62-2001, accept-
able indoor air quality is achieved with air that contains known contaminants at harmful
Figure 10 ASHRAE comfort zone (ASHRAE, 2001).