Page 245 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 245
230 Mechanics and analysis of composite maferials
that was used above to derive Eqs. (5.5). This approach involves strain-displace-
ment equations, Eqs. (2.22),
in conjunction with Hooke’s law
or
where A,, and a,,, are stiffness and compliance coefficients, respectively. The
problem is associated with Eqs. (5.2) which specify only approximate dependence
of displacements u, and uy on coordinate z (actual distribution of ux and uy through
the layer thickness is not known) and must not be differentiated with respect to z.
So we cannot substitute Eqs. (5.2) into Eqs. (5.9) which include derivatives of u,
and uy with respect to z. To see what can happen if we violate this well-known
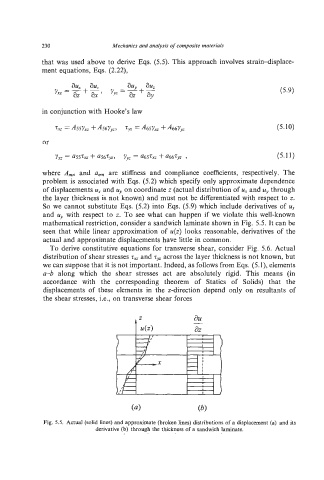
mathematical restriction, consider a sandwich laminate shown in Fig. 5.5. It can be
seen that while linear approximation of u(z) looks reasonable, derivatives of the
actual and approximate displacements have little in common.
To derive constitutive equations for transverse shear, consider Fig. 5.6. Actual
distribution of shear stresses z,, and zp across the layer thickness is not known, but
we can suppose that it is not important. Indeed, as follows from Eqs. (5.1), elements
a-b along which the shear stresses act are absolutely rigid. This means (in
accordance with the corresponding theorem of Statics of Solids) that the
displacements of these elements in the z-direction depend only on resultants of
the shear stresses, Le., on transverse shear forces
(a) (b)
Fig. 5.5. Actual (solid lines) and approximate (broken lines) distributions of a displacement (a) and its
derivative (b) through the thickness of a sandwich laminate.