Page 45 - Mechanics Analysis Composite Materials
P. 45
30 Merhanics and analysis of composite materials
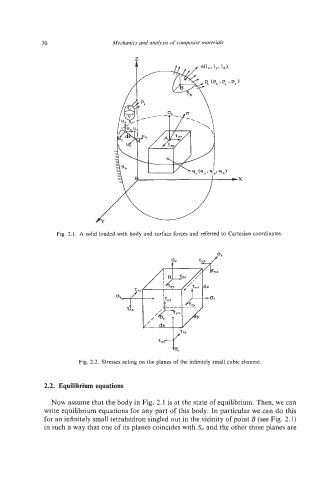
Fig. 2.1. A solid loaded with body and surface forces and referred to Cartesian coordinates.
7ZY
Tzx-
Fig. 2.2. cubic element.
2.2. Equilibrium equations
Now assume that the body in Fig. 2.1 is at the state of equilibrium. Then, we can
write equilibrium equations for any part of this body. In particular we can do this
for an infinitely small tetrahedron singled out in the vicinity of point B (see Fig. 2.1)
in such a way that one of its planes coincides with S, and the other three planes are