Page 226 - Mechanics of Asphalt Microstructure and Micromechanics
P. 226
218 Ch a p t e r Sev e n
LOG| |
Failure
Temperature influence
-2
Non-
Linear Rutting for cyclic
stress loadings from 0
Deformability
-4
Linear
Viscoelasticity Fatigue
-6
LOG(N)
1 2 3 4 5 6
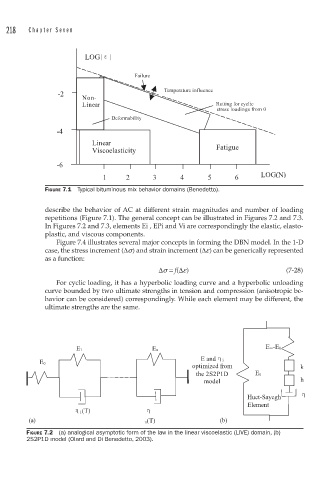
FIGURE 7.1 Typical bituminous mix behavior domains (Benedetto).
describe the behavior of AC at different strain magnitudes and number of loading
repetitions (Figure 7.1). The general concept can be illustrated in Figures 7.2 and 7.3.
In Figures 7.2 and 7.3, elements Ei , EPi and Vi are correspondingly the elastic, elasto-
plastic, and viscous components.
Figure 7.4 illustrates several major concepts in forming the DBN model. In the 1-D
case, the stress increment (Δs) and strain increment (Δe) can be generically represented
as a function:
Δs = f(Δe) (7-28)
For cyclic loading, it has a hyperbolic loading curve and a hyperbolic unloading
curve bounded by two ultimate strengths in tension and compression (anisotropic be-
havior can be considered) correspondingly. While each element may be different, the
ultimate strengths are the same.
E -E0
E1 En
E and i
E 0
optimized from k
the 2S2P1D E 0
model h
Huet-Sayegh
Element
1(T)
(a) n(T) (b)
FIGURE 7.2 (a) analogical asymptotic form of the law in the linear viscoelastic (LIVE) domain, (b)
2S2P1D model (Olard and Di Benedetto, 2003).