Page 219 - Mechanics of Microelectromechanical Systems
P. 219
206 Chapter 4
and consider that the displacement input is the same for both sensors,
namely: Equation (4.38) can be written in this case as:
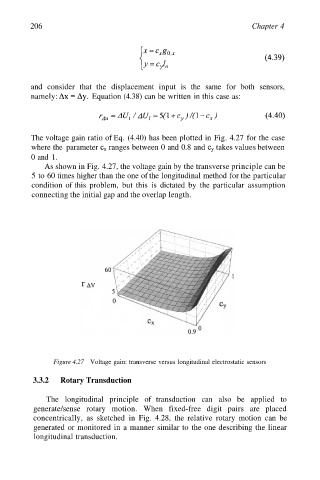
The voltage gain ratio of Eq. (4.40) has been plotted in Fig. 4.27 for the case
where the parameter ranges between 0 and 0.8 and takes values between
0 and 1.
As shown in Fig. 4.27, the voltage gain by the transverse principle can be
5 to 60 times higher than the one of the longitudinal method for the particular
condition of this problem, but this is dictated by the particular assumption
connecting the initial gap and the overlap length.
Figure 4.27 Voltage gain: transverse versus longitudinal electrostatic sensors
3.3.2 Rotary Transduction
The longitudinal principle of transduction can also be applied to
generate/sense rotary motion. When fixed-free digit pairs are placed
concentrically, as sketched in Fig. 4.28, the relative rotary motion can be
generated or monitored in a manner similar to the one describing the linear
longitudinal transduction.