Page 146 - Mechanism and Theory in Organic Chemistry
P. 146
Strengths of Weak Brensted Bases
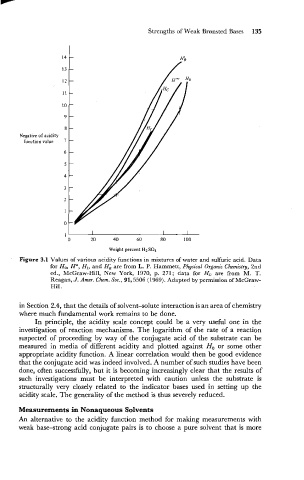
Negative of acidity
function value
Weight percent H2S04
Figure 3.1 Values of various acidity functions in mixtures of water and sulfuric acid. Data
for Ho, H", HI, and Hi are from L. P. Hammett, Physical Organic Chemistry, 2nd
ed., McGraw-Hill, New York, 1970, p. 271; data for H, are from M. T.
Reagan, J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 91,5506 (1969). Adapted by permission of McGraw-
Hill.
in Section 2.4, that the details of solvent-solute interaction is an area of chemistry
where much fundamental work remains to be done.
In principle, the acidity scale concept could be a very useful one in the
investigation of reaction mechanisms. The logarithm of the rate of a reaction
suspected of proceeding by way of the conjugate acid of the substrate can be
measured in media of different acidity and plotted against H, or some other
appropriate acidity function. A linear correlation would then be good evidence
that the conjugate acid was indeed involved. A number of such studies have been
done, often successfully, but it is becoming increasingly clear that the results of
such investigations must be interpreted with caution unless the substrate is
structurally very closely related to the indicator bases used in setting up the
acidity scale. The generality of the method is thus severely reduced.
Measurements in Nonaqueous Solvents
An alternative to the acidity function method for making measurements with
weak base-strong acid conjugate pairs is to choose a pure solvent that is more