Page 153 - Mechanism and Theory in Organic Chemistry
P. 153
.T = 0 x=l
Reaction coordinate
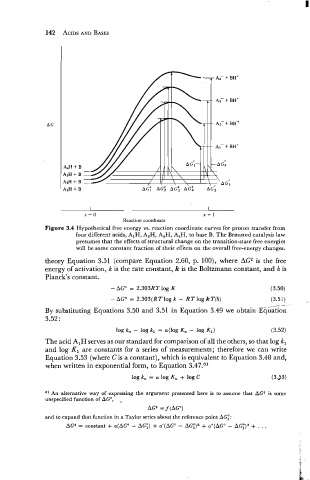
Figure 3.4 Hypothetical free energy vs. reaction coordinate curves for proton transfer from
four different acids, AIH, A2H, A,H, A4H, to base B. The Brcinsted catalysis law
presumes that the effects of structural change on the transition-state free energies
will be some constant fraction of their effects on the overall free-energy changes.
theory Equation 3.51 (compare Equation 2.60, p. loo), where AG* is the free
energy of activation, k is the rate constant, k is the Boltzmann constant, and h is
Planck's constant.
- AGO = 2.303RT log K (3.50)
- AG* = 2.303(RT log k - RT log k T/h) (3.51) -
-/-~
By substituting Equations 3.50 and 3.51 in Equation 3.49 we obtain Equation
3.52 :
log k, - log kl = ci(1og Kn - log Kl) (3.52)
The acid AIH serves as our standard for comparison of all the others, so that log k,
and log K1 are constants for a series of measurements; therefore we can write
Equation 3.53 (where C is a constant), which is equivalent to Equation 3.48 and,
when written in exponential form, to Equation 3.47.61
log kn = ci log Kn + log C (3.93)
" An alternative way of expressing the argument presented here is to assume that AG* is some
unspecified function of AGO, -
AG* = f (AGO)
and to expand that function in a Taylor series about the reference point AGY:
AG* = constant + a(AGO - AGT) + a'(AGo - AGY)a + a"(AGo - AG33 + . . .