Page 207 - Mechatronics for Safety, Security and Dependability in a New Era
P. 207
Ch40-I044963.fm Page 191 Tuesday, August 1, 2006 8:21 PM
1, 2006
8:21 PM
Page 191
Tuesday, August
Ch40-I044963.fm
191
191
Configuration of ISA-4
ISA-4 is largely composed of a Motor unit and a Gear unit as shown in Figure 3. The Gear unit has
precise gears, and the Motor unit consists of Rotor Magnet, Stator Core, and three circuit modules. Each
circuit module has its own function as Control module, Communication module, or Power module.
The Control module manages all TSA-4 functions such as servo control or safety management, the
Communication module manages the communication between the Control module and the CPU (Cen-
tral Processing Unit) in the upper layer which controls the robot's whole body motion, and the Power
module works as motor drive circuit and is very compact and efficient.
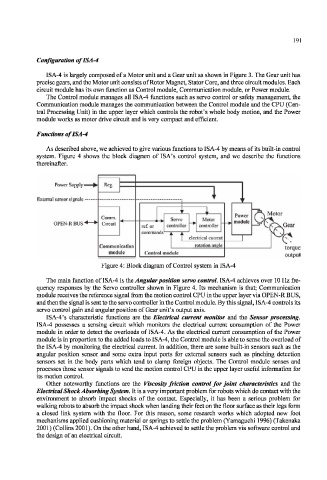
Functions of ISA-4
As described above, we achieved to give various functions to ISA-4 by means of its built-in control
system. Figure 4 shows the block diagram of ISA's control system, and we describe the functions
thereinafter.
Power Supply • Reg.
-.xternal sensor signals r
;
T 1 (^\ Motor
Power
Comm. Servo Motor
OPEN-RBUS-*—• Circuit module
ref. or controller controller
• T electrical current
Communication rotation angle
module Control module output
Figure 4: Block diagram of Control system in ISA-4
The main function of ISA-4 is the Angular position servo control. ISA-4 achieves over 10 Hz fre-
quency responses by the Servo controller shown in Figure 4. Its mechanism is that; Communication
module receives the reference signal from the motion control CPU in the upper layer via OPEN-R BUS,
and then the signal is sent to the servo controller in the Control module. By this signal, ISA-4 controls its
servo control gain and angular position of Gear unit's output axis.
ISA-4's characteristic functions are the Electrical current monitor and the Sensor processing.
ISA-4 possesses a sensing circuit which monitors the electrical current consumption of the Power
module in order to detect the overloads of ISA-4. As the electrical current consumption of the Power
module is in proportion to the added loads to TSA-4, the Control module is able to sense the overload of
the ISA-4 by monitoring the electrical current. In addition, there are some built-in sensors such as the
angular position sensor and some extra input ports for external sensors such as pinching detection
sensors set in the body parts which tend to clamp foreign objects. The Control module senses and
processes those sensor signals to send the motion control CPU in the upper layer useful information for
its motion control.
Other noteworthy functions are the Viscosity friction control for joint characteristics and the
Electrical Shock Absorbing System. It is a very important problem for robots which do contact with the
environment to absorb impact shocks of the contact. Especially, it has been a serious problem for
walking robots to absorb the impact shock when landing their feet on the floor surface as their legs form
a closed link system with the floor. For this reason, some research works which adopted new foot
mechanisms applied cushioning material or springs to settle the problem (Yamaguchi 1996) (Takenaka
2001) (Collins 2001). On the other hand, ISA-4 achieved to settle the problem via software control and
the design of an electrical circuit.